Create a Runbook
Runbooks in Harness AI SRE enable you to automate incident response workflows, operational procedures, and remediation actions. This comprehensive guide walks you through creating, configuring, and deploying effective runbooks that can significantly reduce mean time to resolution (MTTR) and improve your team's operational efficiency.
Before You Begin
Prerequisites
Ensure you have the following before creating your first runbook:
- Platform Access: Active Harness AI SRE account with appropriate permissions.
- User Permissions: Required Account, Organisation and Project level permissions.
- Integration Access: Configured integrations for the tools you plan to use (Slack, Jira, ServiceNow, etc.).
- Monitoring Setup: Alert sources configured (Datadog, New Relic, PagerDuty, etc.).
Key Concepts
Before diving into runbook creation, familiarize yourself with these core concepts:
- Actions: Individual tasks or operations within a runbook (notifications, API calls, pipeline executions).
- Triggers: Conditions that automatically initiate runbook execution.
- Variables: Dynamic values that can be passed between actions and customized per execution.
- Sequences: The order in which actions are executed within your workflow.
Creating Your Runbook
- Interactive Guide
- Step by Step
Follow this interactive guide to create automated runbooks with actions, workflows, and integrations.
Step 1: Access Runbooks
- Click on Runbooks from the left panel in your Harness AI SRE platform
- This will take you to the runbooks management interface
Step 2: Create New Runbook
- Click New Runbook to start creating your automated workflow
- This opens the runbook creation interface
Step 3: Configure Basic Details
- Fill in the essential details for your runbook:
- Name: Use a descriptive name (e.g., "High CPU Alert Response", "Database Connection Recovery")
- Description: Clearly explain the runbook's purpose and when it should be used
- Provide clear, meaningful information that helps team members understand the runbook's function
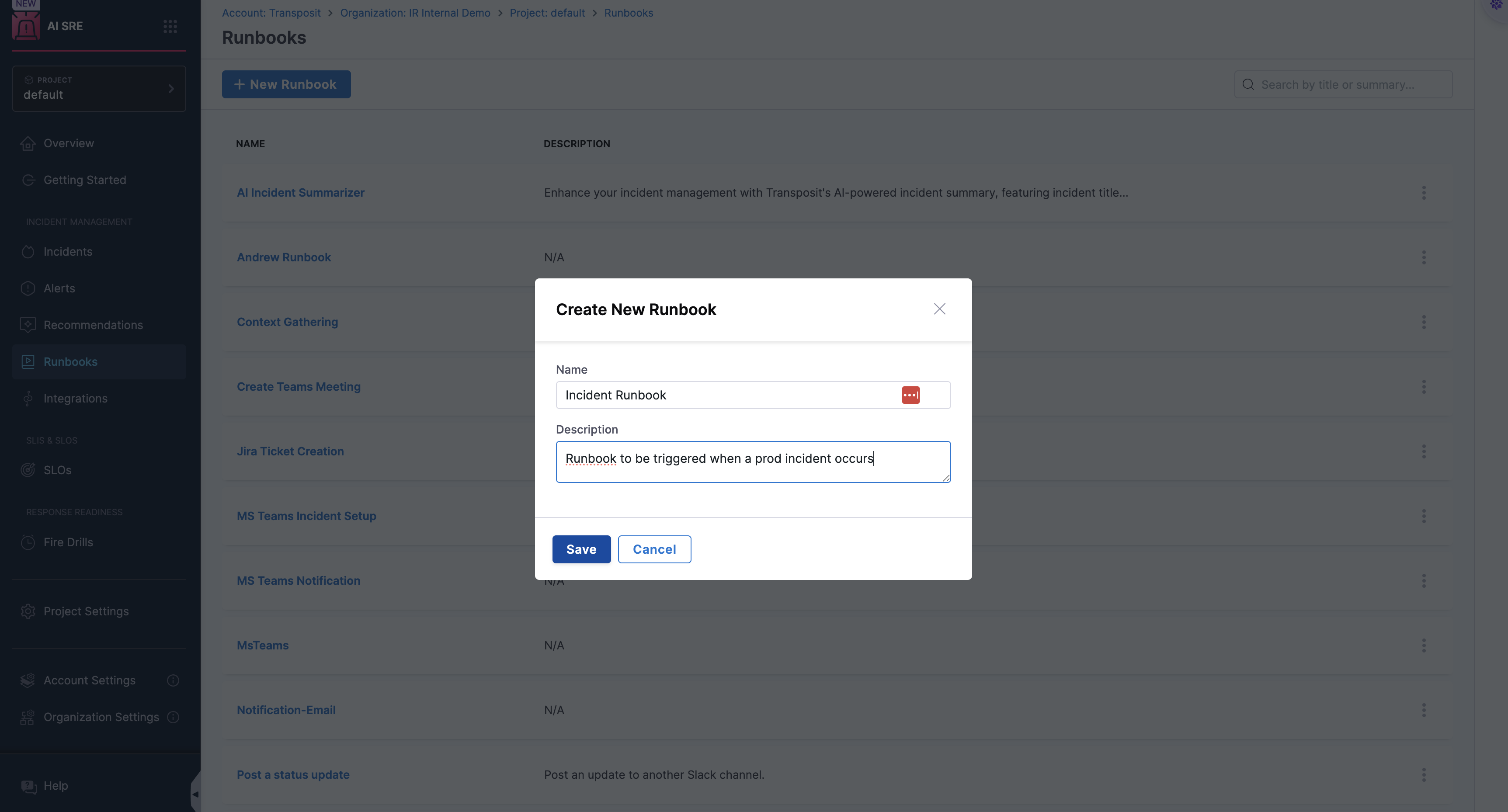
Step 4: Save Initial Configuration
- Click Save to create the basic runbook structure
- This establishes your runbook and opens the workflow designer
Step 5: Add Your First Action
- Click New Action to add steps to your runbook workflow
- This opens the action selection interface where you can choose from various automation categories
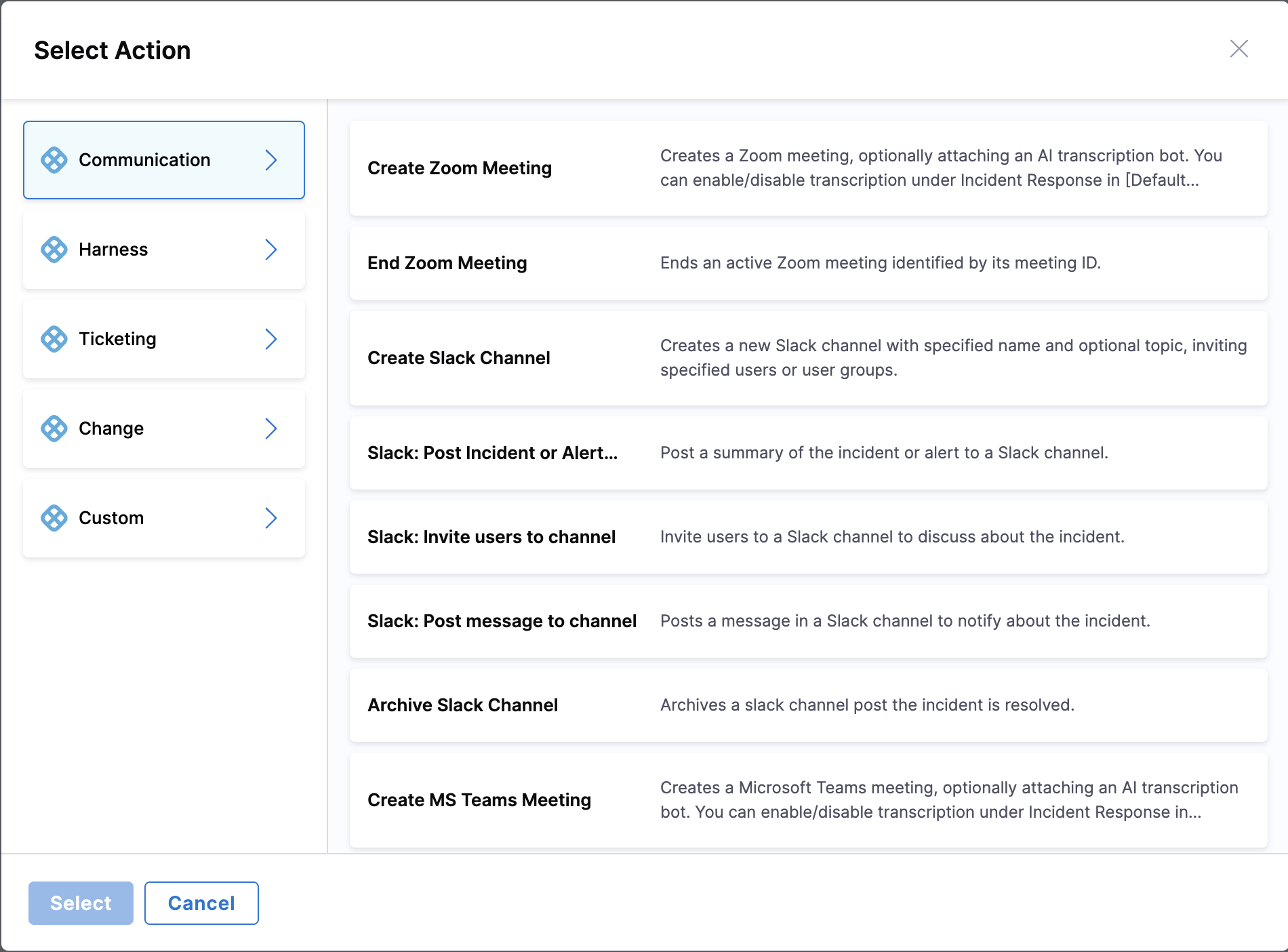
Step 6: Explore Action Categories
-
The left panel displays different action categories:
- Communication: Slack, MS Teams, Zoom, and Email
- Harness: Pipeline execution, feature flags, deployments
- Ticketing: Jira, ServiceNow
- Change: GitHub pull requests, code changes
- Alerting and On-Call: OpsGenie, PagerDuty
- Lifecycle: Key events, managing incident timeline, resolving alerts, and closing incidents
-
Browse through categories to find the appropriate action for your workflow
Step 7: Select and Configure Action
- Choose any action from the available list in your selected category
- Click Select to add the action to your workflow
- Each action will have specific configuration requirements based on its functionality
Step 8: Configure Input/Output Context
You can configure the context to determine which fields will be available in the data picker when setting up action parameters:
- Select Context Type: Choose the Incident or Alert Context (Any/No/Custom) based on your runbook's purpose
- Choose Specific Type: For Custom Incident or Alert Context:
- Select the appropriate Incident Type from the dropdown for incident-based runbooks
- Select the appropriate Alert Type from the dropdown for alert-based runbooks
- Field Availability Impact:
- Basic Context (Any/No): Data picker shows only standard incident/alert fields
- Specific Incident Type: Data picker displays both basic fields AND custom fields defined for that incident type
- Specific Alert Type: Data picker displays both basic fields AND custom fields defined for that alert type
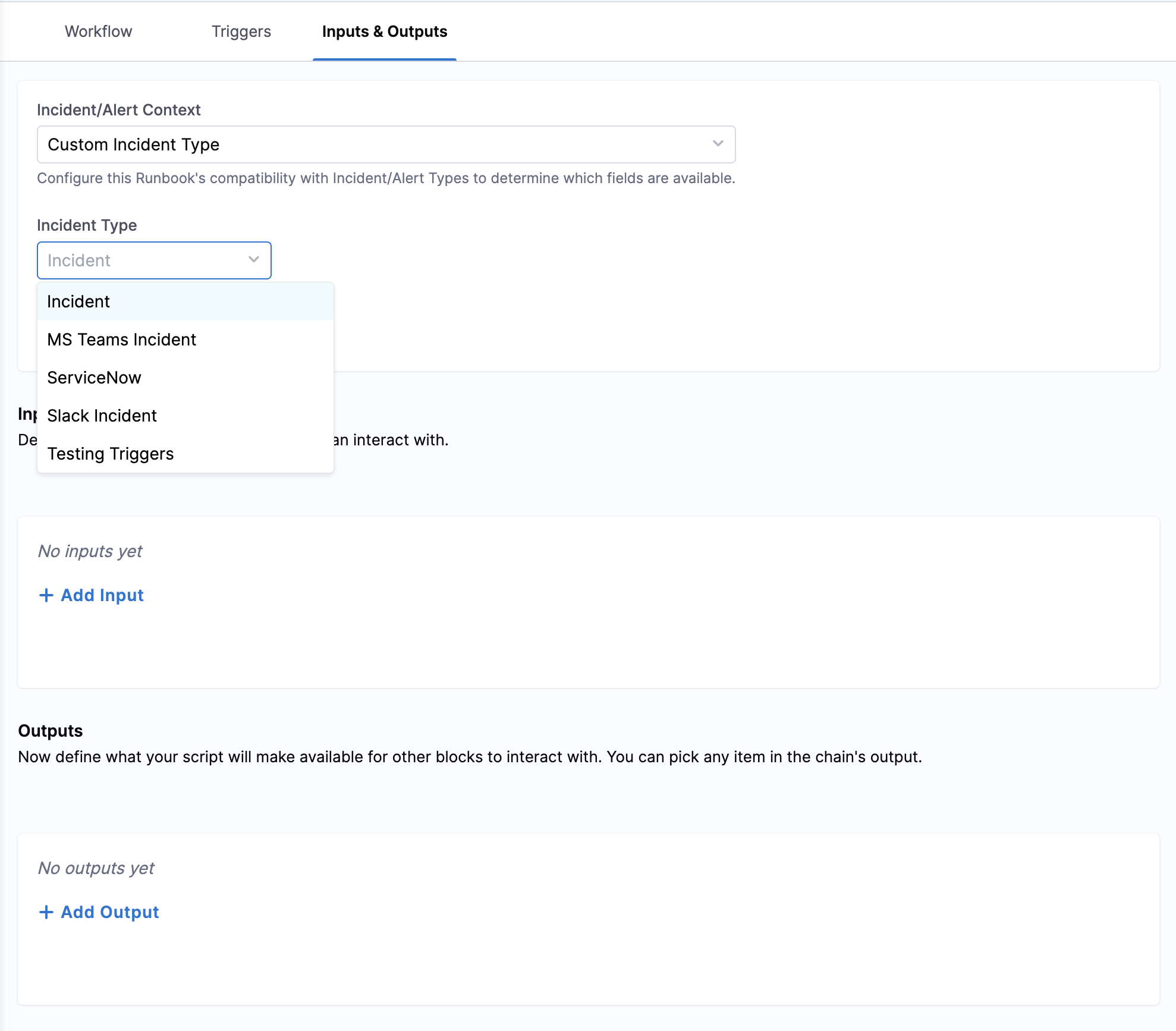
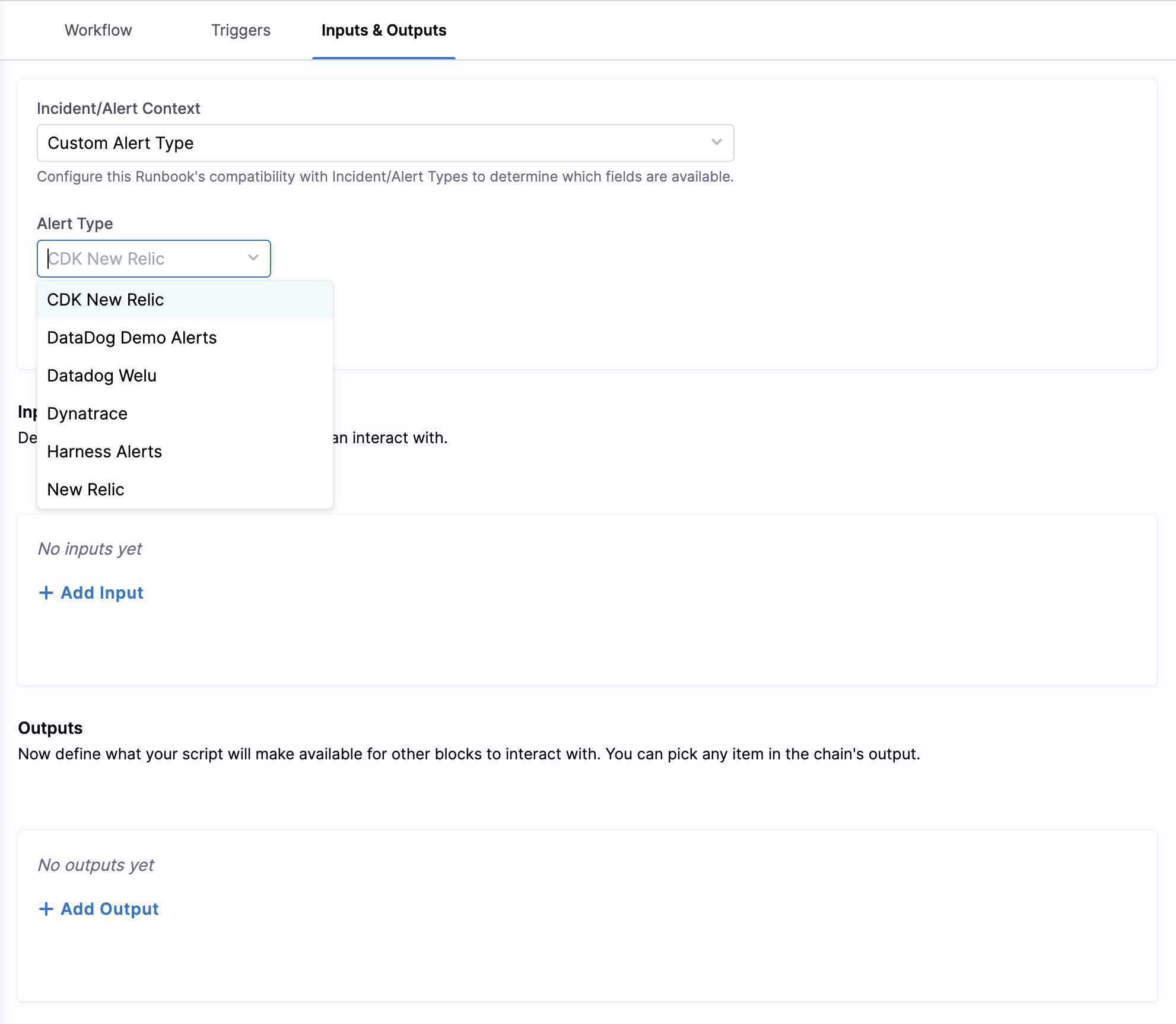
Why This Matters: The context selection directly affects what data will be available when configuring your action parameters. Choosing a specific incident type ensures you have access to all custom fields defined for that type, making your runbook more powerful and context-aware.
Variable Configuration Details
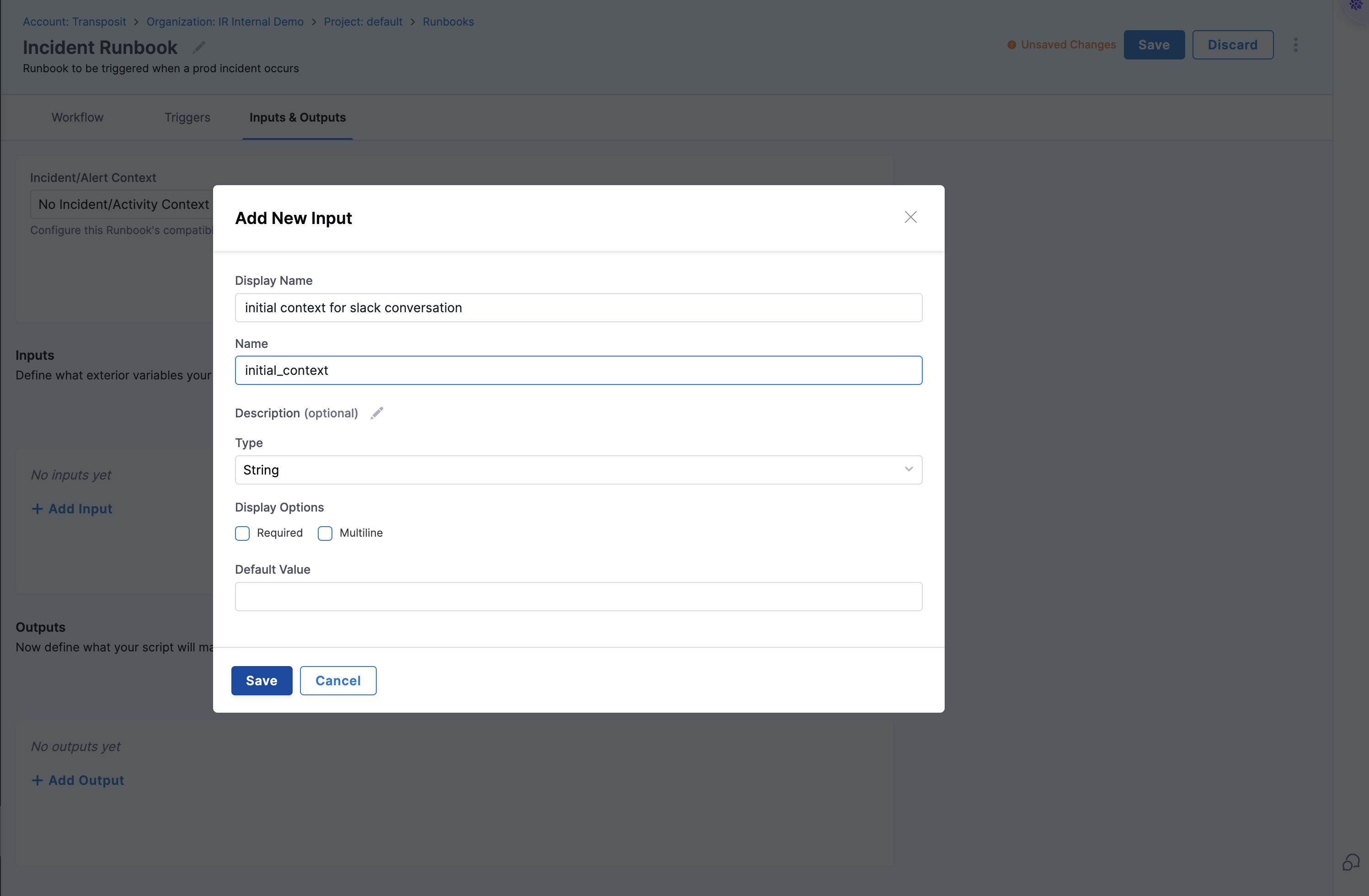
When configuring Input/Output context, you can also define custom variables:
- Input Variables: Values provided when the runbook is triggered, must be defined based on the incident or alert context
- Output Variables: Results from action executions, must be defined based on the action execution
- Required Fields: Name, Display Name, Description, Type, and Default Value
- Data Types: String, Integer, Number, Boolean, Object, or Array
- Requirement Level: Variables can be defined as required or optional based on the use case
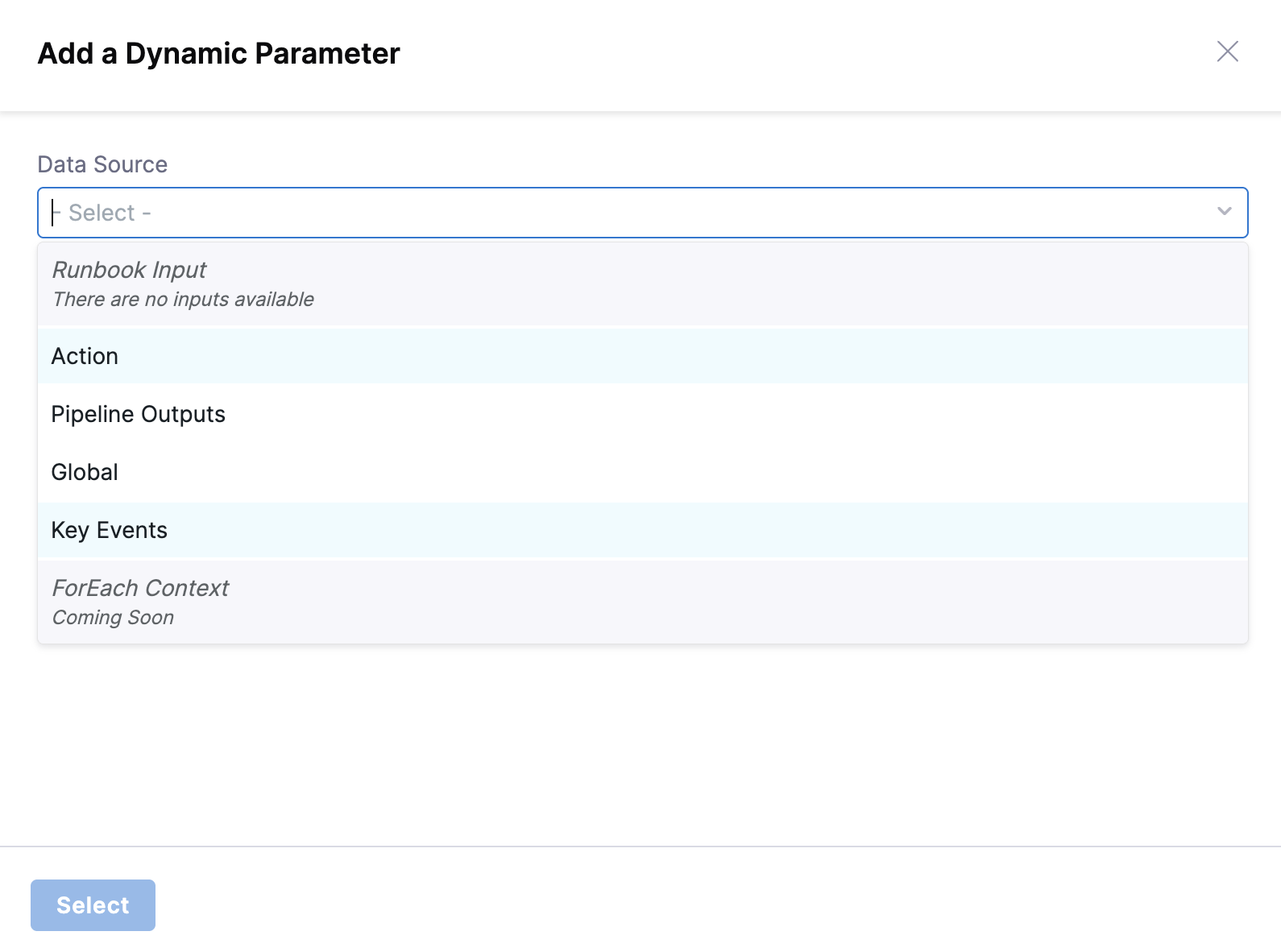
Dynamic Parameter Sources Available
Once context is configured, the data picker will provide access to multiple dynamic data sources:
- Runbook Inputs: Variables defined in the Input/Output section
- Action Outputs: Results from previously executed actions
- Pipeline Outputs: Data from Harness pipeline executions
- Global Variables: System-wide variables available to all runbooks
- Key Events: Event-driven data that can trigger specific behaviors
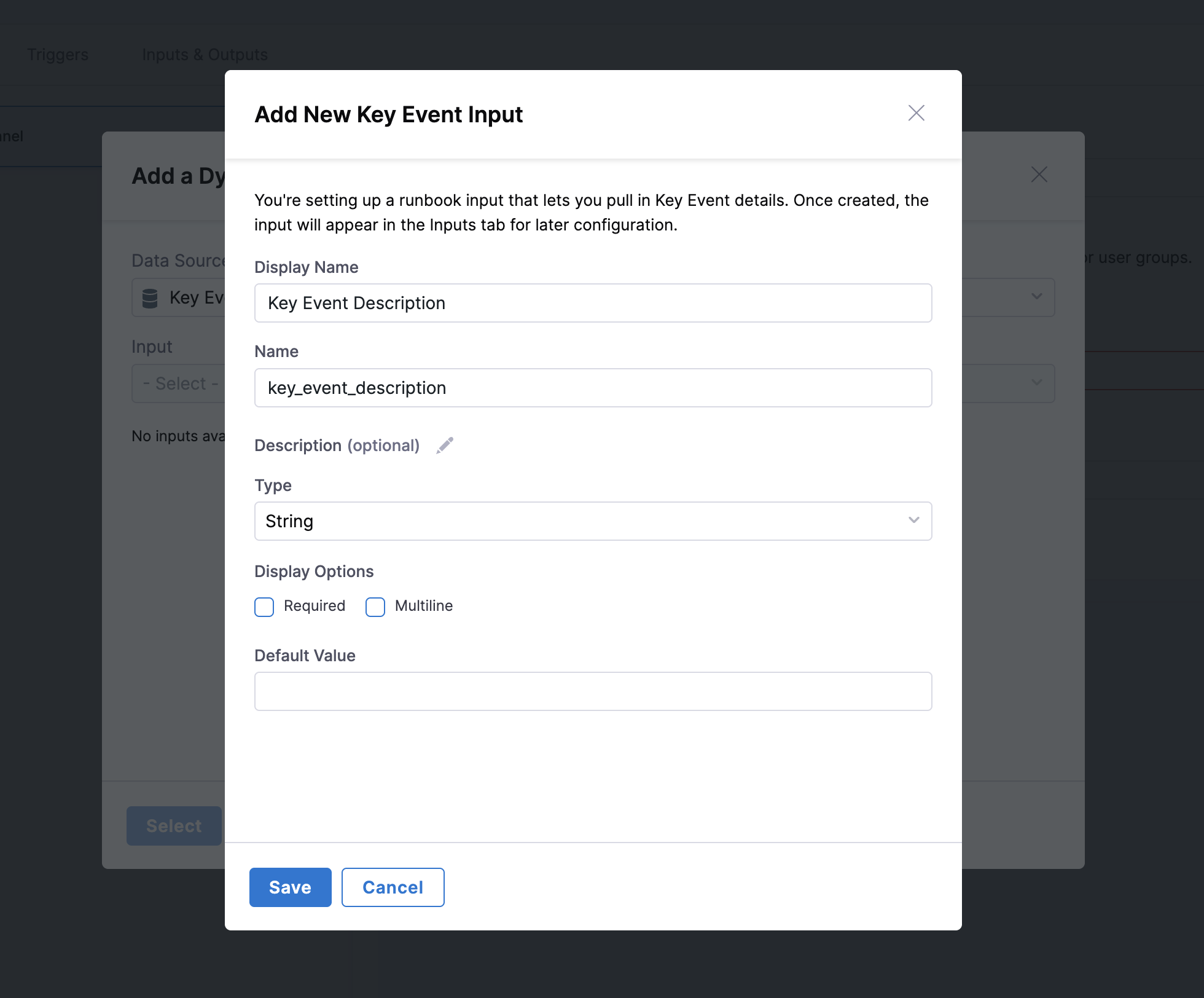
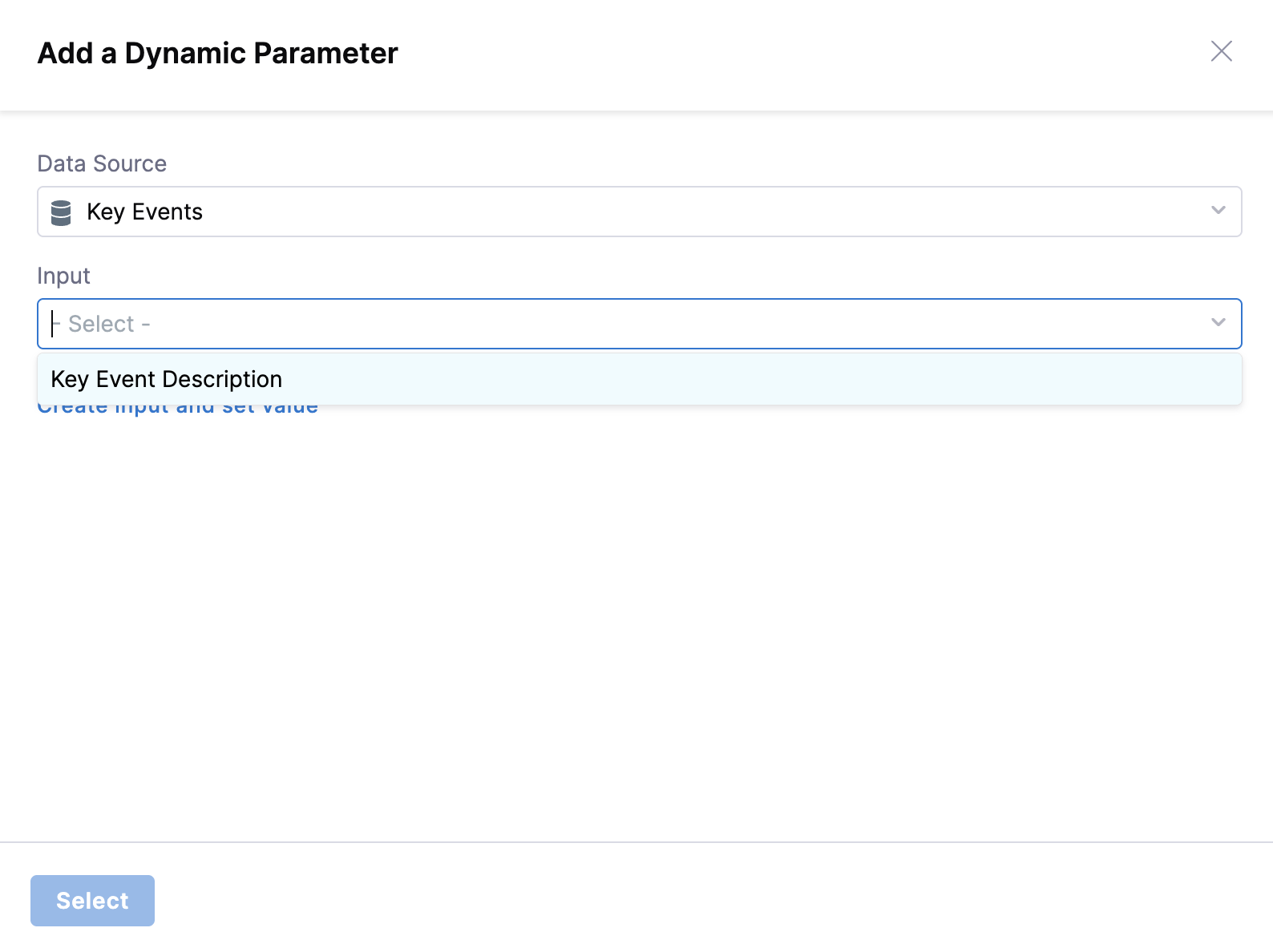
Key Event Integration Setup
For event-driven runbooks, you can configure Key Events directly:
- Select Key Event as Source: When configuring an action parameter, choose "Key Event" as the data source
- Create Input and Set Value: Create inputs directly without navigating to Input/Output section:
- Click "Create Input and Set Value"
- Provide a Display Name, Type, and Default Value
- Save the new input variable
- Select the Key Event text from the input dropdown
Step 9: Configure Action Parameters
- Click on the Data picker to fill in values for the action's input fields
- The data picker will now show fields based on your Input/Output context selection:
- Basic fields (always available): Standard incident/alert properties
- Custom fields (if specific type selected): Additional fields defined for your chosen incident/alert type
- Configure parameters specific to your chosen action:
- Static Values: Enter fixed values for consistent behavior
- Dynamic Values: Use variables for flexible, context-aware execution
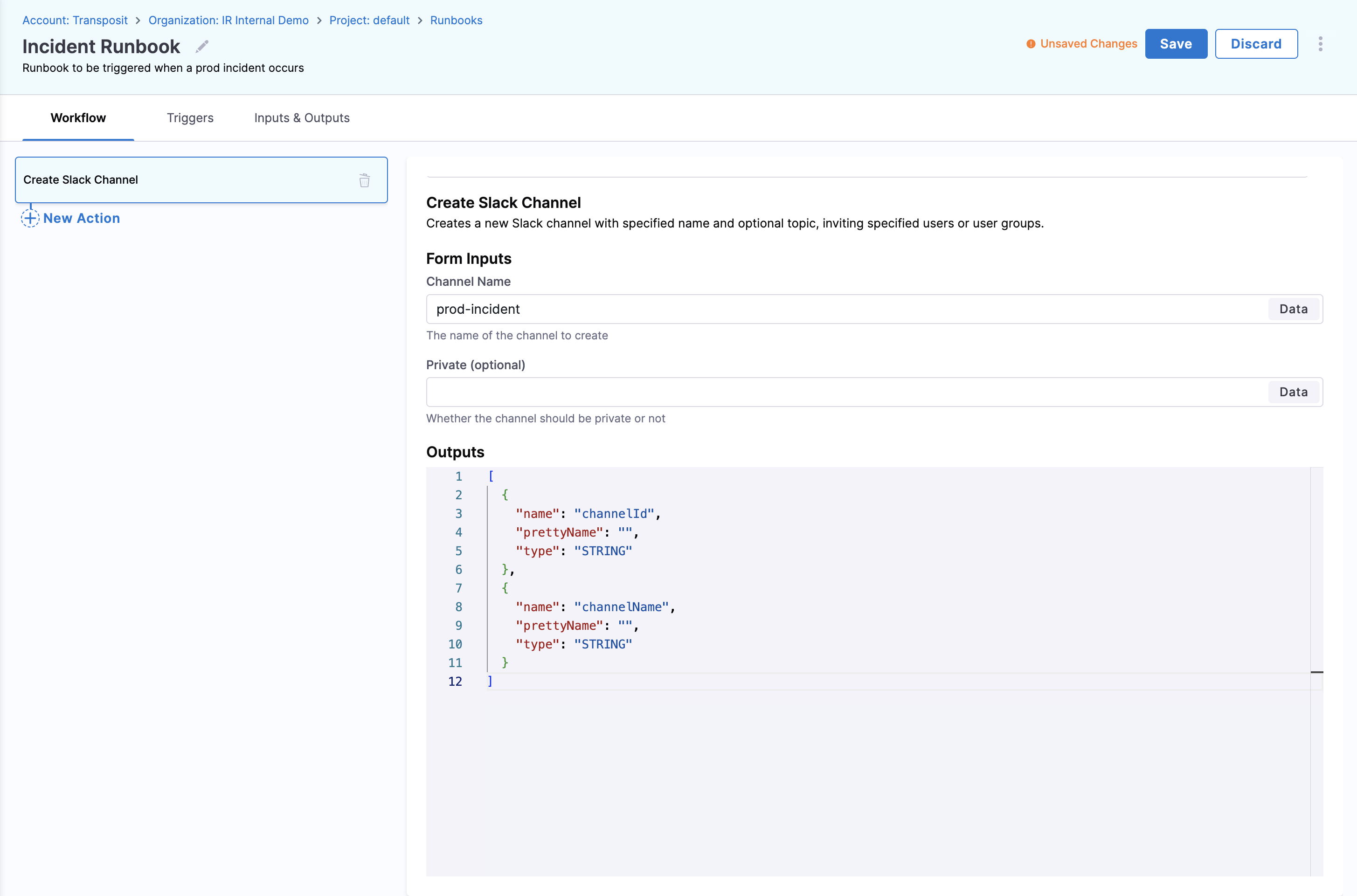
Step 10: Use Dynamic Data Sources
- Select from available data source options (now configured in Step 8):
- Runbook Input: Variables defined for the runbook
- Action Outputs: Results from previously executed actions
- Pipeline Outputs: Data from Harness pipeline executions
- Global Values: System-wide variables available to all runbooks
- Choose the appropriate data source based on your workflow requirements
Step 11: Build Complete Workflow
- Click New Action to add more steps based on your workflow needs
- Click Action to access the action library again
- Click Select for each action you want to add
- Repeat the configuration process for each action:
- Configure parameters
- Set up data sources
- Define action sequences
- Arrange actions in logical order for effective execution
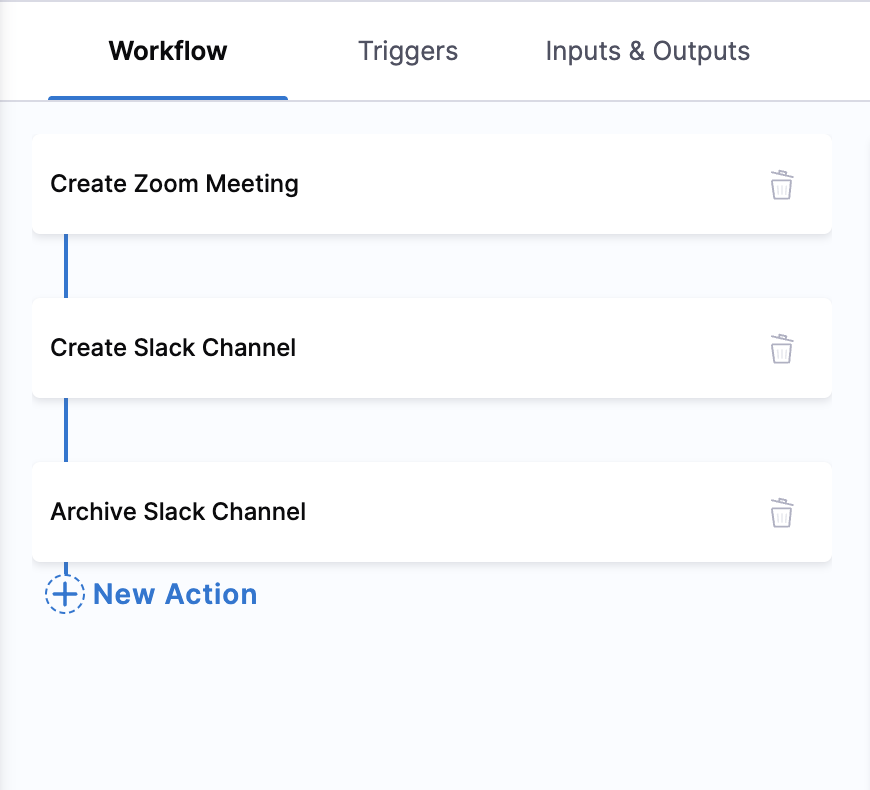
Best Practices for Action Sequencing:
- Immediate Response: Start with critical notifications and incident creation
- Information Gathering: Follow with diagnostic and monitoring actions
- Remediation: Execute fix actions based on gathered information
- Validation: Verify that remediation was successful
- Closure: Update stakeholders and close incidents
Step 12: Save Your Runbook
- Click Save from the top right corner to finalize your runbook configuration
- Your runbook is now ready for testing and deployment
- All configured actions and workflows are preserved for future execution
Advanced Configuration
For advanced trigger configuration including Key Events, conditional logic, and complex automation scenarios, refer to the comprehensive Create a Runbook Trigger guide.
Available Actions and Integrations
Harness AI SRE provides a comprehensive library of pre-built actions across multiple categories. Choose the right combination of actions to build effective automation workflows.
Communication & Collaboration Tools
Establish immediate communication channels and keep stakeholders informed throughout incident resolution.
Slack Integration
- Send Notifications: Broadcast alerts to channels or direct messages.
- Create Channels: Automatically create incident-specific channels.
- Start Threads: Organize discussions and updates.
- Add Members: Add members to the channel.
- Archive Channels: Clean up after incident resolution.
Microsoft Teams Integration
- Send Messages: Send alerts to specific teams or channels.
- Create Meetings: Automatically create Teams meeting, optionally attaching an AI transcription bot.
Zoom Integration
- Create Meetings: Instantly set up incident response calls, optionally attaching an AI transcription bot.
- End Meetings: End an active Zoom meeting.
Incident Response & Ticketing Systems
Automate incident tracking, assignment, and resolution workflows across your preferred ticketing platforms.
Jira Integration
- Issue Creation: Automatically create tickets with relevant context.
- Status Updates: Progress incidents through workflow states.
- Update Tickets: Updates an existing Jira issue's summary, description, issue type, or adds a comment with relevant context.
ServiceNow Integration
- Incident Management: Create and manage ServiceNow incidents.
- Change Requests: Initiate emergency or standard changes.
- Update Incidents: Updates an existing ServiceNow incident's summary, description, issue type, or adds a comment with relevant context.
Automation & Pipeline Execution
Execute remediation actions, deploy fixes, and trigger operational workflows.
Harness Pipelines Integration
- Pipeline Execution: Trigger deployment or remediation pipeline.
- Feature Flag Management: Deploy specific versions or rollback changes.
- Environment Management: Manage infrastructure scaling or configuration.
Configure Triggers
Triggers determine when and how your runbooks execute automatically. For comprehensive trigger configuration including interactive guides and detailed setup instructions, see:
Create a Runbook Trigger - Complete guide for configuring automated runbook execution based on incidents, alerts, and key events.
Quick Trigger Setup
- Access Trigger Configuration: Click the Triggers tab in your runbook editor
- Add Trigger: Click + New Trigger to begin the trigger setup process
- Choose Trigger Template: Select the template from the incident types
- Define Conditions: Set specific conditions for runbook activation
- Test and Deploy: Validate trigger logic before production deployment
Note: Multiple triggers can be added to a single runbook based on your use case requirements.
Test Your Runbook
Thorough testing is essential before deploying runbooks to production. A well-tested runbook prevents failures during critical incidents and ensures reliable automation.
Testing Steps
- Select an Alert or Incident: Go to AI SRE → Alerts or Incidents in your Harness platform, then select the alert or incident you want to test.
- Select a Runbook: Click the Runbooks tab and select the runbook you want to test.
- Execute Runbook: In case of no associated runbooks, click Execute Runbook to begin the testing process.
- Test Runbook: Click Execute to begin the testing process.
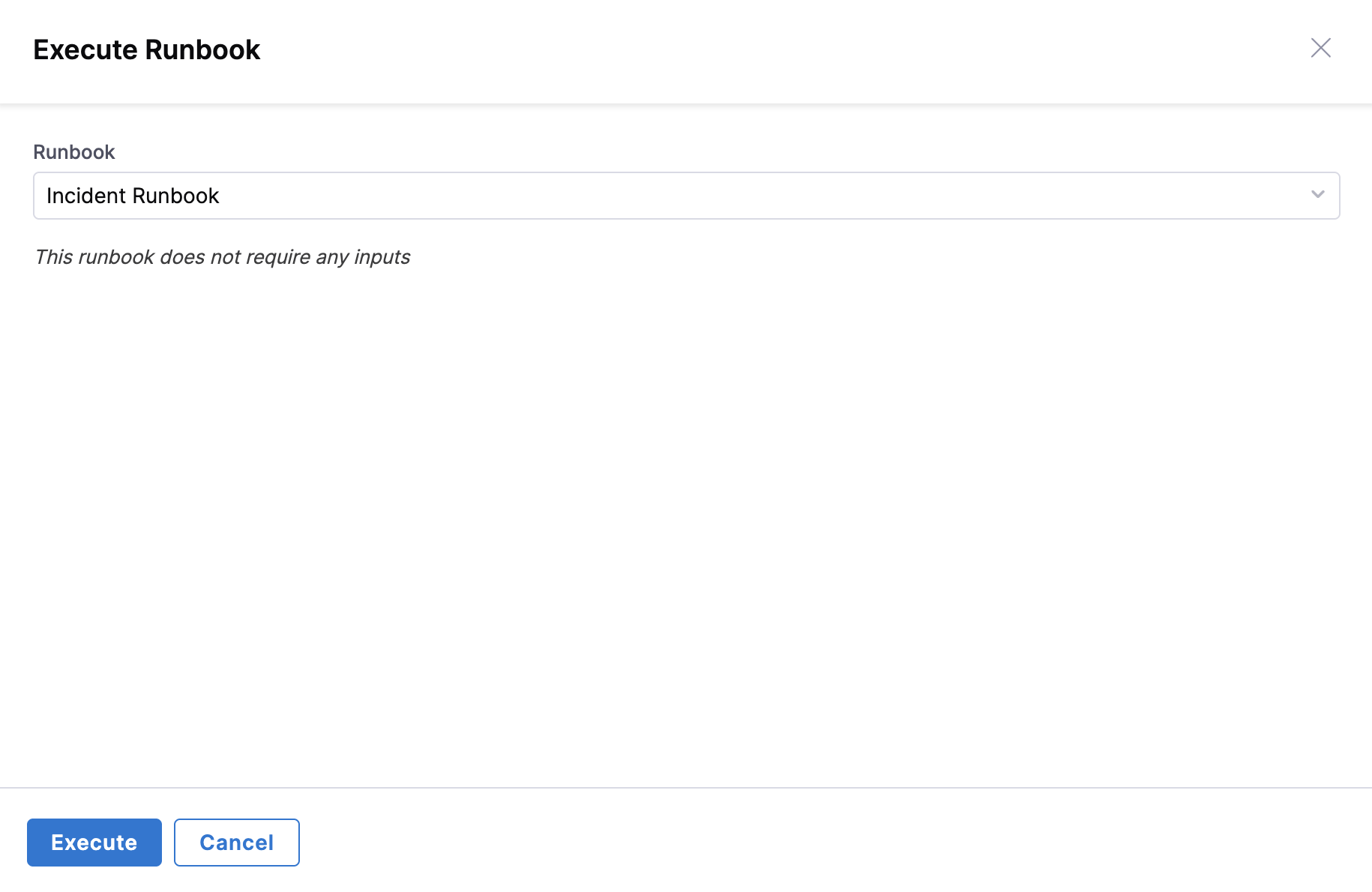
Pre-Production Testing
1. Environment Preparation
- Test Environment: Set up a dedicated testing environment that mirrors production.
- Test Data: Prepare realistic test scenarios and data sets.
- Integration Sandboxes: Use test instances of integrated tools (Slack, Jira, etc.).
- Mock Services: Create mock endpoints for external dependencies.
2. Functional Testing
- Action Validation: Verify each action executes correctly with expected parameters.
- Sequence Testing: Confirm actions execute in the correct order.
- Variable Passing: Validate that variables are correctly passed between actions.
- Error Handling: Test failure scenarios and error recovery mechanisms.
3. Integration Testing
- Notification Delivery: Confirm all notifications reach intended recipients.
- Pipeline Executions: Verify that triggered pipelines complete successfully.
- API Responses: Check that external API calls return expected results.
- Authentication: Ensure all integrations authenticate properly.
4. End-to-End Testing
- Complete Workflows: Execute full runbook scenarios from trigger to completion.
- Multiple Scenarios: Test various input combinations and edge cases.
- Performance Testing: Measure execution times and resource usage.
- Concurrent Execution: Test behavior when multiple instances run simultaneously.
Testing Checklist
- All actions execute without errors.
- Notifications are delivered to correct channels/recipients.
- Variables are properly populated and passed.
- External integrations respond as expected.
- Error conditions are handled gracefully.
- Execution logs provide sufficient detail for troubleshooting.
- Performance meets acceptable thresholds.
- Security permissions are correctly enforced.
Deploy and Monitor
Once testing is complete, deploy your runbook to production and establish monitoring to ensure continued effectiveness.
Deployment Process
- Final Review: Conduct a final review of runbook configuration and testing results.
- Stakeholder Approval: Obtain necessary approvals from the team.
- Production Deployment: Activate the runbook in your production environment.
- Documentation Update: Update operational documentation with runbook details.
Best Practices for Runbook Creation
Design Principles
- Start Simple: Begin with basic workflows and gradually add complexity as you gain experience.
- Modular Design: Create reusable actions and workflows that can be combined for different scenarios.
- Clear Naming: Use descriptive names for runbooks, actions, and variables that clearly indicate their purpose.
Operational Excellence
- Regular Updates: Review and update runbooks regularly to reflect changes in infrastructure and processes.
- Timeout Configuration: Set appropriate timeouts to prevent runbooks from hanging indefinitely.
- Conditional Logic: Use conditional statements to avoid unnecessary action execution.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Execution Failures
Problem: Runbook actions fail to execute
- Solution: Check integration credentials and network connectivity.
- Prevention: Implement health checks and credential rotation.
Problem: Variables not passing between actions
- Solution: Verify variable names and data types match expectations.
- Prevention: Use consistent naming conventions and validate variable mappings.
Performance Issues
Problem: Runbooks execute slowly
- Solution: Optimize action sequences and enable parallel execution where possible.
- Prevention: Regular performance testing and monitoring.
Next Steps
Advanced Configuration
- Create a Runbook Trigger: Set up automated runbook execution based on incidents, alerts, and events.
- Configure Authentication: Set up secure access to integrated tools and services.
- Configure Incident Fields: Customize incident data collection and processing.
- Return to Overview: Explore additional runbook capabilities and features.
Integration Setup Guides
Communication & Collaboration
- Slack Integration: Complete setup guide for Slack automation.
- Microsoft Teams Integration: Configure Teams notifications and collaboration.
- Zoom Integration: Set up automated meeting creation and management.
Incident Management
- Jira Integration: Automate issue tracking and project management.
- ServiceNow Integration: Integrate with enterprise service management.
Automation & Pipelines
- Harness Pipelines Integration: Execute deployment and remediation pipelines.
Need Help? Contact our support team by email at support@harness.io or visit the Harness Documentation for additional resources and troubleshooting guides.