Artifact Registry and Continuous Integrations
Learn how to use Artifact Registry with the Continuous Integration (CI) module.
Build and push to Docker with Artifact Registry
Harness CI offers a Build and push to Docker step that allows you to build and push a docker image to any registry. Usually, this requires a connector to the registry you want, but with AR you can connect to a registry directly, within the platform, without any complicated setup.
- Interactive guide
- Step-by-step
To do so, follow these steps:
- Navigate to your pipeline, and enter your
Buildstage. - Create a new
Build and Push an image to Docker Registrystep. Harness Artifact Registryis the default registry type. Ensure that it is selected, and move to the next step.- Select your registry under
Registry. Clicking the field will show a list of available registries. - Once your registry is selected, a list of images will populate under
Image Name. Choose one, or type the name of a new image that you are building the first time. - Enter any image tags you wish under
Tags. - Click
Apply Changesat the top right, and you are done! No connectors needed.
Upload Artifacts to Harness Artifact Registry
Harness CI provides a native Upload Artifacts to Harness Artifact Registry step that simplifies the process of publishing artifacts directly to your Harness Artifact Registry. This dedicated step supports multiple package types and eliminates the need for complex scripting or external connectors.
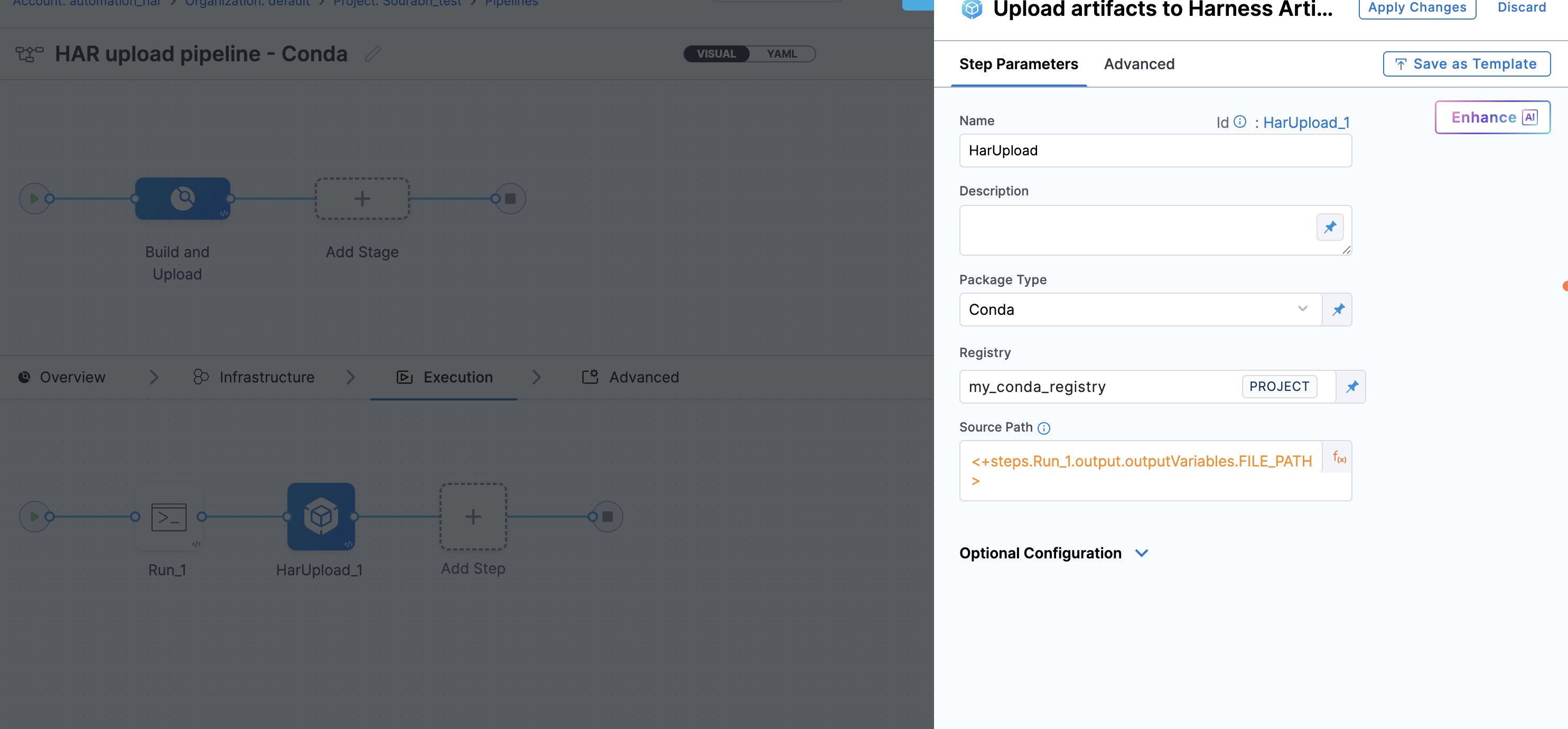
The Upload Artifacts step allows you to configure artifact uploads through a simple interface. You can specify the package type, target registry, and source path for your artifacts. The source path typically points to artifacts generated from a previous step in your pipeline, such as a Run step that builds, creates, or downloads packages.
Enter the Source Path where your artifact is located:
- This path typically references the output from a previous step, such as:
/harness/target/*.jarfor Maven artifacts/harness/example.tar.gzfor npm tarballs/harness/build/for Python wheels
- You can use expressions to reference outputs from earlier steps
Package-specific requirements:
- Generic packages: Requires explicit package name and version
- Go packages: Requires explicit version specification
The Upload Artifacts step uses Harness CLI internally to upload artifacts to Harness Artifact Registry, ensuring consistent behavior and authentication across all package types.
Example YAML
pipeline:
name: Upload Conda Package to Artifact Registry
identifier: conda_upload_pipeline
projectIdentifier: default_project
orgIdentifier: default
stages:
- stage:
name: Build and Upload
identifier: build_upload_stage
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Run
name: Download Conda Package
identifier: download_conda_package
spec:
shell: Sh
command: |-
#!/bin/sh
set -e
# Configuration
PACKAGE_NAME="docutils-stubs"
CHANNEL="conda-forge"
echo "Fetching metadata for ${PACKAGE_NAME} from ${CHANNEL}"
# Fetch package metadata
JSON_DATA=$(curl -s "https://api.anaconda.org/package/${CHANNEL}/${PACKAGE_NAME}/files")
# Extract the first download URL
LATEST_URL=$(echo "${JSON_DATA}" \
| grep -o '"download_url": "[^"]*"' \
| head -n 1 \
| cut -d'"' -f4)
# Validate URL
if [ -z "${LATEST_URL}" ]; then
echo "Failed to retrieve download URL"
exit 1
fi
# Normalise protocol if required
case "${LATEST_URL}" in
//* ) LATEST_URL="https:${LATEST_URL}" ;;
esac
FILE_NAME=$(basename "${LATEST_URL}")
echo "Downloading ${FILE_NAME}"
# Download artifact
curl -L "${LATEST_URL}" -o "${FILE_NAME}"
# Resolve absolute path
FILE_PATH="$(pwd)/${FILE_NAME}"
echo "Resolved artifact path: ${FILE_PATH}"
# Write output using Harness supported contract
echo "FILE_PATH=${FILE_PATH}" >> "${DRONE_OUTPUT}"
- step:
type: HarUpload
name: Upload to Artifact Registry
identifier: upload_to_registry
spec:
registryRef: my_conda_registry
packageType: CONDA
sourcePath: <+steps.download_conda_package.output.outputVariables.FILE_PATH>
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Arm64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
Key Points:
- Step 1 (Run): Downloads a Conda package from conda-forge and outputs the file path using
DRONE_OUTPUT - Step 2 (HarUpload): References the output variable from Step 1 using
<+steps.download_conda_package.output.outputVariables.FILE_PATH>and uploads to the specified registry - Package Type: Set to
CONDAto ensure proper indexing in Artifact Registry - Source Path: Dynamically references the downloaded artifact location from the previous step
Add a Run or Plugin Step to Your CI Pipeline
Seamlessly reference artifacts stored in Harness Artifact Registry within your CI Run and Plugin steps. This functionality eliminates the need for an external connector, providing a streamlined and user-friendly experience, while enabling efficient and simplified workflows.
- Interactive guide
- Step-by-step
To do so, follow these steps:
- Navigate to your pipeline, and enter your
Buildstage. - Create a new
Runstep. Harness Artifact Registryis the default registry type. Ensure that it is selected, and move to the next step.- Select your registry under
Registry. Clicking the field will show a list of available registries. - Enter your artifact's
imageName:version. - Add your run command, e.g. `echo "Run step completed".
- Click
Apply Changes.
To verify the Run or Plugin step executes as expected, run the pipeline.