Redis cache penetration
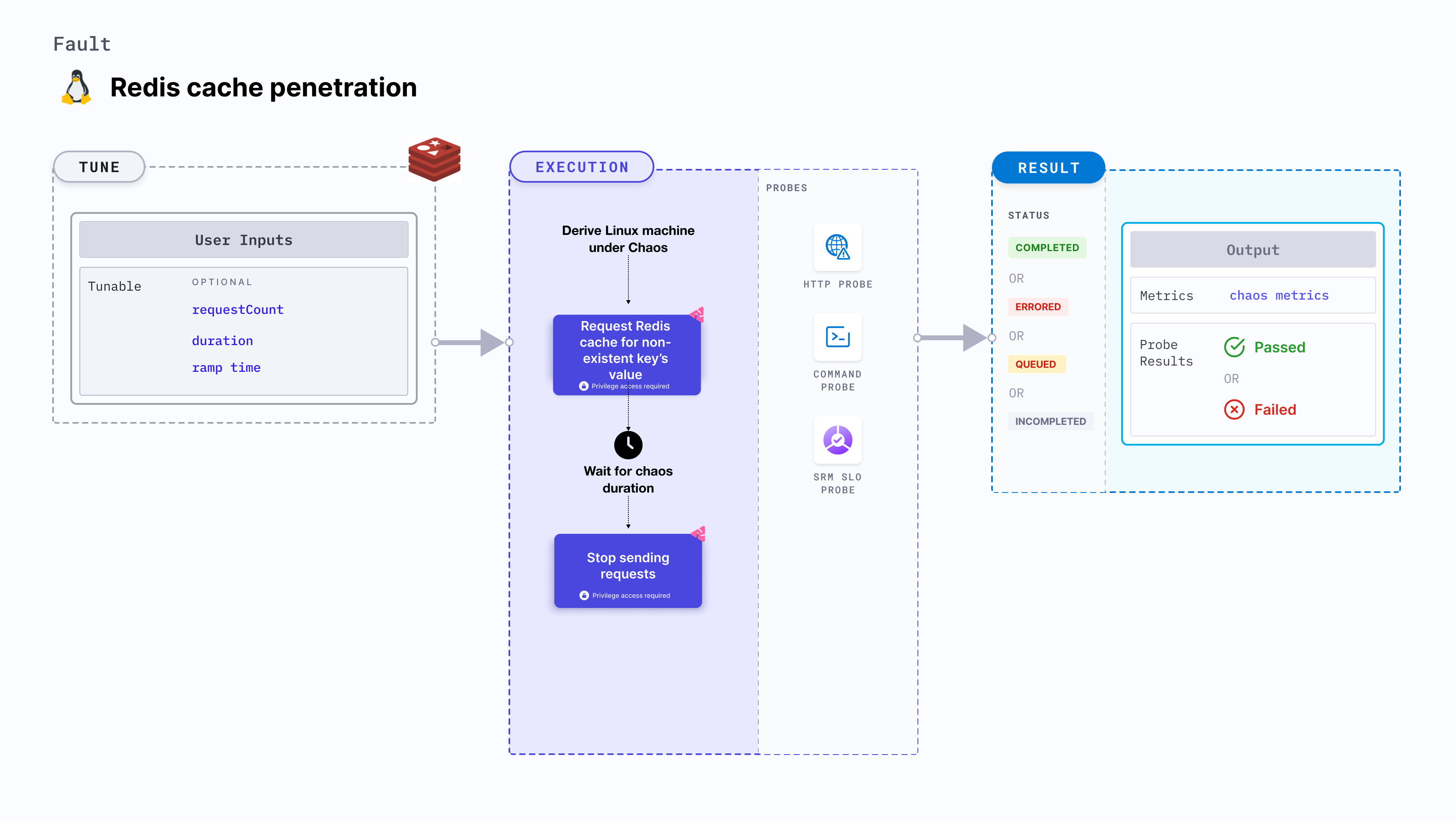
Redis cache penetration fault continuously sends cache requests to the Redis database to find the value for a non-existing key. This continuous request reduces the performance of the application.
Use cases
- Slows down the database for responses to other requests.
- Determines the resilience of Redis-dependant application when cache requests are continuously sent to a Redis database and they result in a cache miss.
- This fault can be executed on Ubuntu 16 or higher, Debian 10 or higher, CentOS 7 or higher, RHEL 7 or higher, Fedora 30 or higher, and openSUSE LEAP 15.4 or higher.
- The
linux-chaos-infrastructuresystemd service should be in an active state, and the infrastructure should be inCONNECTEDstate.
Fault permissions
The fault uses the root Linux user and root user group.
Redis authentication
If your Redis server doesn't require authentication, you may directly provide the address tunable. Refer here.
The following authentication and connection details reside on the same machine where the chaos infrastructure is executed. These details are provided in the /etc/linux-chaos-infrastructure/redis.env file in the following format:
ADDRESS="127.0.0.1:6379"
PASSWORD=XXXXXXXX
TLS_AUTH_CERT="/path/to/tls-cert"
ADDRESSis a mandatory field. You can also includePASSWORDandTLS_AUTH_CERTfields. You need them only if you have configured your Redis database to facilitate authentication.
| ENV name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ADDRESS | Location where the Redis server is running. | redis-server.com |
| PASSWORD | Password to connect to the Redis database. | password |
| TLS_AUTH_CERT | File path to the location where the TLS certificate is stored. | /path/to/file |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| address | The address of the Redis server. | If a password or certificate is also required alongside the address, please use the secret file approach. |
| requestCount | Number of requests to be sent for accessing the cache. | Default: 1000. For more information, go to request count. |
| duration | Duration through which chaos is injected into the target resource. Should be provided in [numeric-hours]h[numeric-minutes]m[numeric-seconds]s format. | Default: 30s. Examples: 1m25s, 1h3m2s, 1h3s. For more information, go to duration. |
| rampTime | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos. Should be provided in [numeric-hours]h[numeric-minutes]m[numeric-seconds]s format. | Default: 0s. Examples: 1m25s, 1h3m2s, 1h3s. For more information, go to ramp time. |
Number of requests
The requestCount input variable indicates the number of requests sent to access the Redis cache. Redis cache. Its default value is 1000.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this input variable:
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: redis-cache-penetration
labels:
name: cache-penetration
spec:
redisChaos/inputs:
duration: 30s
requestCount: 1000
rampTime: ""