Kubernetes releases and versioning for deployments (configmaps secrets)
This topic describes how Harness tracks releases and versions for Kubernetes deployments.
Every Harness deployment creates a new release with an incrementally increasing number. Release history is stored in the Kubernetes cluster in a ConfigMap or Secret. ConfigMap or Secret are essential for release tracking, versioning, and rollback.
By default, all ConfigMaps and Secrets are versioned by Harness. The corresponding references for these ConfigMaps and Secrets in other manifest objects are also updated (for example, managed workloads like Deployment, and so on). Versioning does not change how you use ConfigMaps or Secrets. You need not reference the release numbers when using ConfigMaps or Secrets.
You can see the use of release numbers and versioning in the logs of the deployment in the prepare section of the logs, (Current release number is 7, Previous Successful Release is 6):
Manifests processed. Found following resources:
Kind Name Versioned
Secret harness-v1 true
Secret harness-v1-dckrcfg false
ConfigMap harness-v1 true
Service harness-v1-svc false
Deployment harness-v1-deployment false
Ingress harness-v1-ingress false
IngressRoute harness-v1-ingress-rt false
Current release number is: 7
Previous Successful Release is 6
In some cases, you might want to skip versioning. For example, skip versioning for:
- ImagePullSecret because it never changes.
- TLS certs if they are referred in a Kubernetes container command or arguments.
For cases where versioning is not required, it can be skipped by using these two ways:
- Annotate the manifest provided in the Harness service's Manifests section with
harness.io/skip-versioning: "true". - In the Harness service's Manifest Configuration page, select Manifests > Advanced, and then select the Skip Versioning checkbox.
Versioning is not done when declarative rollback is enabled.
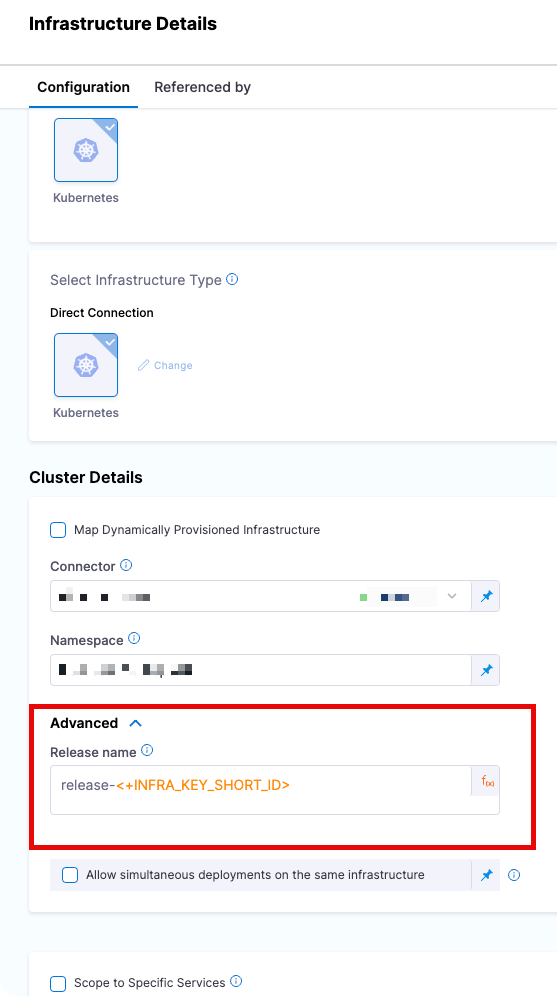
Release Name
Harness also uses a release name for tracking releases. These release names should be unique for your deployments and pipelines.
Do not change the release name value between deployments unless absolutely necessary. The release name is used by Harness for tracking releases of app versions and rollback. If you change the release name value between deployments, this will reset the versioning number and will stop rollbacks up to that point (breaking the versioning chain)
Not having a unique release name could affect licensing. Please ensure your release names are unique.
You can supply a release name in a stage's infrastructure Release Name setting.
During deployment Harness creates a ConfigMap listing the resources of the release and uses the Release name for tracking them. You can see this within your Kubernetes cluster, in the namespace if you run kubectl get configmap
> $ kubectl get configmap
NAME DATA AGE
kube-root-ca.crt 1 176d
release-78a47e 2 176d
release-05ea23 7 176d
Harness suggests utilizing a Release Name which is formed from a combination of release- and a unique string created using the Harness expression <+INFRA_KEY>.
The release name must be unique across the cluster. release-<+INFRA_KEY> ensures a unique name.
If the name is not defined properly, and is not unique across the cluster, there is a danger of collision in the versioning between the two different deployments.
For example, Pipeline A can increment the versioning of Pipeline B's configmap/secrets and add its own versions to the same series if the release name is not unique. This will cause a break in the versions and will cause issues in rollbacks.
When declarative rollback is enabled, the corresponding Secret name format is harness.release.<release-name>.<release-number>.
Release name is used to create the corresponding Harness release ConfigMap or Secret. Therefore, the provided release name should be a valid DNS subdomain name.