GitOps Sync with Multiple Rollout Steps
This advanced example demonstrates a complete pipeline that starts with a GitOps sync step followed by multiple GitOps Rollout steps, showing how to pass values between steps.
Overview
Harness provides a powerful expression system to access outputs from previous steps. This enables dynamic configuration where steps automatically discover and use the correct rollout details without hardcoding values.
Key Benefits
- Dynamic Configuration: Steps automatically discover and use the correct rollout details
- Reusability: The same pipeline can work across different environments and applications
- Error Reduction: No hardcoded values that could become outdated
- Maintainability: Changes to rollout names or namespaces are automatically reflected
Pipeline Overview
Here's a visual representation of the pipeline:
To use Argo Rollouts with Harness GitOps pipelines, ensure the CDS_GITOPS_ENABLE_ROLLOUTS_PIPELINE_UX feature flag is enabled in your Harness account.
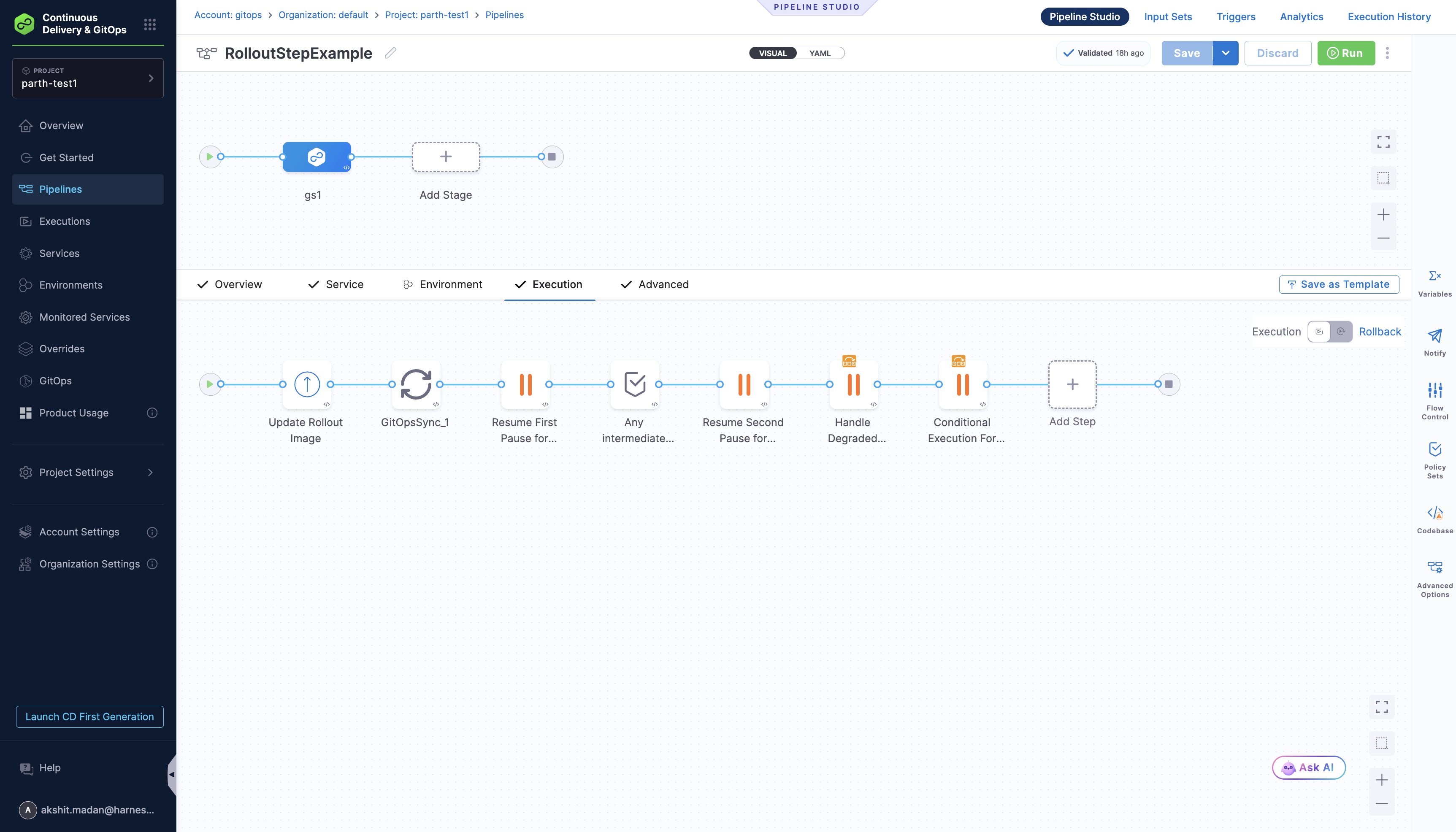
This pipeline consists of the following key steps:
- Update Rollout Image: Updates the image tag in your GitOps Application's manifest
- GitOps Sync: Synchronizes the GitOps Application to apply the image update, which triggers a new rollout
- Resume First Pause for Rollout: Resumes the rollout from the first pause step
- Any Intermediate Steps: Optional placeholder steps for custom logic
- Resume Second Pause for Rollout: Resumes the rollout from the second pause step
- Handle Degraded Rollout: Handles degraded rollout states with retry action
- Conditional Execution For Rollout: Conditional execution based on application name
Pipeline YAML
pipeline:
name: RolloutStepExample
identifier: RolloutStepExample
projectIdentifier: projectidentifier
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: gs1
identifier: gs1
description: ""
type: Deployment
spec:
deploymentType: Kubernetes
gitOpsEnabled: true
service:
serviceRef: svc1
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: UpdateGitOpsApp
name: Update Rollout Image
identifier: Update_Rollout_Image
spec:
targetRevision: master
kustomize:
images:
- argoproj/load-tester:latest
- argoproj/rollouts-demo:yellow
replicas: []
applicationName: app-rollout-example
agentId: qaargoagent
timeout: 10m
- step:
type: GitOpsSync
name: GitOpsSync_1
identifier: GitOpsSync_1
spec:
prune: false
dryRun: false
applyOnly: false
forceApply: false
applicationsList:
- applicationName: app-rollout-example
agentId: qaargoagent
retryStrategy: {}
retry: false
syncOptions:
skipSchemaValidation: false
autoCreateNamespace: false
pruneResourcesAtLast: false
applyOutOfSyncOnly: false
replaceResources: false
prunePropagationPolicy: foreground
timeout: 10m
- step:
type: GitOpsRollout
name: Resume First Pause for Rollout
identifier: Resume_First_Pause_for_Rollout
spec:
appName: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].appName>
agentIdentifier: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].agentIdentifier>
namespace: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].namespace>
rolloutName: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].rolloutName>
waitUntilHealthStatus:
healthStatus: Suspended
autoRolloutAction: resume
timeout: 10m
failureStrategies:
- onFailure:
errors:
- AllErrors
action:
type: Ignore
- step:
type: Wait
name: Any intermediate steps
identifier: Any_intermediate_steps
spec:
duration: 30s
- step:
type: GitOpsRollout
name: Resume Second Pause for Rollout
identifier: Resume_Second_Pause_for_Rollout
spec:
appName: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].appName>
agentIdentifier: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].agentIdentifier>
namespace: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].namespace>
rolloutName: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].rolloutName>
waitUntilHealthStatus:
healthStatus: Suspended
autoRolloutAction: resume
timeout: 10m
failureStrategies:
- onFailure:
errors:
- AllErrors
action:
type: Ignore
- step:
type: GitOpsRollout
name: Handle Degraded Rollout
identifier: Handle_Degraded_Rollout
spec:
appName: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].appName>
agentIdentifier: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].agentIdentifier>
namespace: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].namespace>
rolloutName: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].rolloutName>
autoRolloutAction: retry
timeout: 10m
when:
stageStatus: Failure
- step:
type: GitOpsRollout
name: Conditional Execution For Rollout
identifier: Conditional_Execution_For_Rollout
spec:
appName: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].appName>
agentIdentifier: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].agentIdentifier>
namespace: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].namespace>
rolloutName: <+execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].rolloutName>
autoRolloutAction: restart
timeout: 10m
when:
stageStatus: All
condition: <+pipeline.stages.gs1.spec.execution.steps.GitOpsSync_1.gitops.applications[0].name>=="app-rollout-example"
rollbackSteps: []
environment:
environmentRef: env1
deployToAll: true
tags: {}
failureStrategies:
- onFailure:
errors:
- AllErrors
action:
type: StageRollback
How to Get Values from Previous Steps
Harness provides a powerful expression system to access outputs from previous steps. Here's how it works:
1. Accessing GitOps Sync Outputs
The GitOps Sync step outputs discovered rollouts that can be used in subsequent steps:
<+execution.steps.<step_identifier>.gitops.discoveredRollouts[<index>].<field>>
Available fields:
agentIdentifier- The GitOps agent identifierappName- The GitOps application namerolloutName- The Rollout resource namenamespace- The namespace where the rollout is deployed
2. Expression Examples
# Get the first discovered rollout's agent
<+execution.steps.gitops_sync_step.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].agentIdentifier>
# Get the rollout name
<+execution.steps.gitops_sync_step.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].rolloutName>
# Get the namespace
<+execution.steps.gitops_sync_step.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].namespace>
3. Multiple Rollouts
If you have multiple rollouts, access them by index:
# First rollout
<+execution.steps.gitops_sync_step.gitops.discoveredRollouts[0].rolloutName>
# Second rollout
<+execution.steps.gitops_sync_step.gitops.discoveredRollouts[1].rolloutName>
4. Accessing Other Step Outputs
You can also access outputs from other step types:
# Access shell script outputs
<+execution.steps.shell_step.output.outputVariables.VAR_NAME>
# Access HTTP response
<+execution.steps.http_step.output.responseBody>
# Access artifact information
<+execution.steps.build_step.output.artifactPath>
Step-by-Step Explanation
Step 1: Update Rollout Image
- Purpose: Updates the container image in your GitOps Application's manifest
- Configuration: Uses the
UpdateGitOpsAppstep to modify the image tag in the rollout manifest - Key Settings:
targetRevision: Git branch containing your manifestskustomize.images: Specify the new image to deployapplicationName: Your GitOps Application nameagentId: GitOps Agent identifier
Step 2: GitOps Sync
- Purpose: Synchronizes the GitOps Application to apply the image update
- Configuration: Uses the
GitOpsSyncstep to trigger a sync operation - Key Settings:
applicationsList: List of applications to syncsyncOptions: Various sync configuration optionstimeout: Maximum time to wait for sync completion
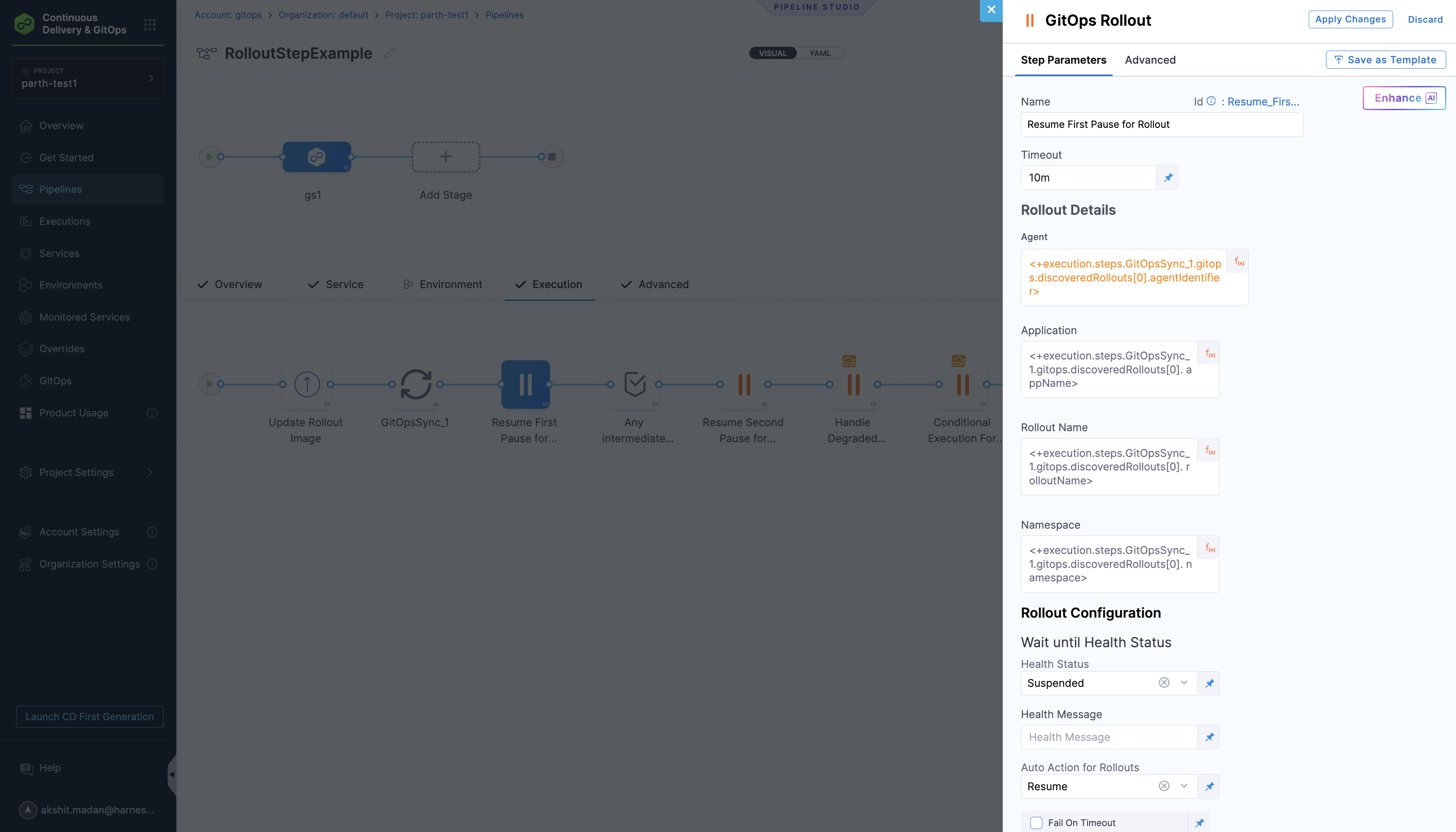
Step 3: Resume First Pause for Rollout
- Purpose: Resumes the rollout from the first pause step
- Configuration: Uses the
GitOpsRolloutstep with resume action - Key Settings:
autoRolloutAction: Set toresumewaitUntilHealthStatus: Set toSuspendedto wait for pause state- Uses expressions from the Sync step to get rollout details
failureStrategies: Ignore errors to continue pipeline
Step 4: Any Intermediate Steps
- Purpose: Placeholder for custom logic or additional processing
- Configuration: Uses the
Waitstep for simple delays - Use Cases:
- Add custom validation logic
- Insert additional processing steps
- Create delays between operations
Step 5: Resume Second Pause for Rollout
- Purpose: Resumes the rollout from the second pause step
- Configuration: Uses the
GitOpsRolloutstep with resume action - Key Settings:
autoRolloutAction: Set toresumewaitUntilHealthStatus: Set toSuspendedto wait for pause state- Uses expressions from the Sync step to get rollout details
Step 6: Handle Degraded Rollout
- Purpose: Handles degraded rollout states with retry action
- Configuration: Uses the
GitOpsRolloutstep with retry action - Key Settings:
autoRolloutAction: Set toretrywhen: Set toFailureto only run on stage failure- Uses expressions from the Sync step to get rollout details
Step 7: Conditional Execution For Rollout
- Purpose: Conditional execution based on application name
- Configuration: Uses the
GitOpsRolloutstep with restart action - Key Settings:
autoRolloutAction: Set torestartwhen: Conditional execution with custom condition- Uses expressions to check application name
Best Practices
- Use descriptive step identifiers for easier reference
- Add timeout values appropriate for your deployment size
- Include health checks for critical production deployments
- Consider manual approval steps for production environments
- Test expressions in the pipeline editor before saving