Add a Harness GitOps repository
This topic describes how to add a Harness GitOps repository containing the declarative description of a desired state.
Harness GitOps repositories are connections to repos containing the declarative description of a desired state. The declarative description can be in Kubernetes manifests, Helm Chart, Kustomize manifests, etc.
A Harness GitOps Repository is used for Harness GitOps only. For other Harness features like CI, CD Pipelines, etc, use a standard Git Connector.
Before you begin
If you are new to Harness GitOps, familiarize yourself with the following topics:
Supported platforms
Currently, the supported GitOps Repository platforms are:
- Git platforms (any Access Token-related connection supported by ArgoCD, including BitBucket)
- HTTP Helm servers
- OCI Helm repositories
Add a repository
In the repository setup, you will select the Agent to use when synching state. Be sure you have a GitOps Agent set up already.
For details, see Install a Harness GitOps Agent.
You will also provide the credentials to use when connecting to the Git repository. Ensure you have your credentials available.
If you use a GitOps repository credentials template with a GitOps repository, then the repository path in the GitOps repository must be a subfolder of the repository path in the repository credentials template.
-
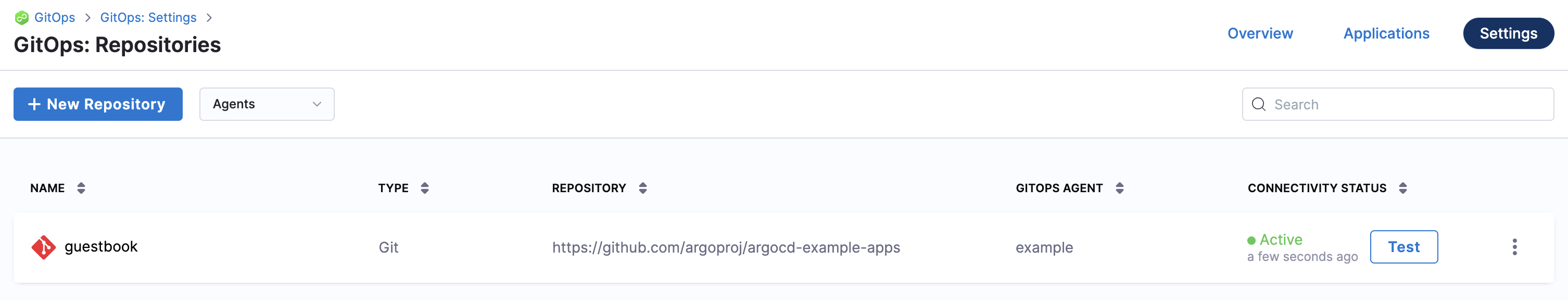
In your Harness project, select GitOps, and then select Settings.
-
Select Repositories.
-
Select New Repository.
-
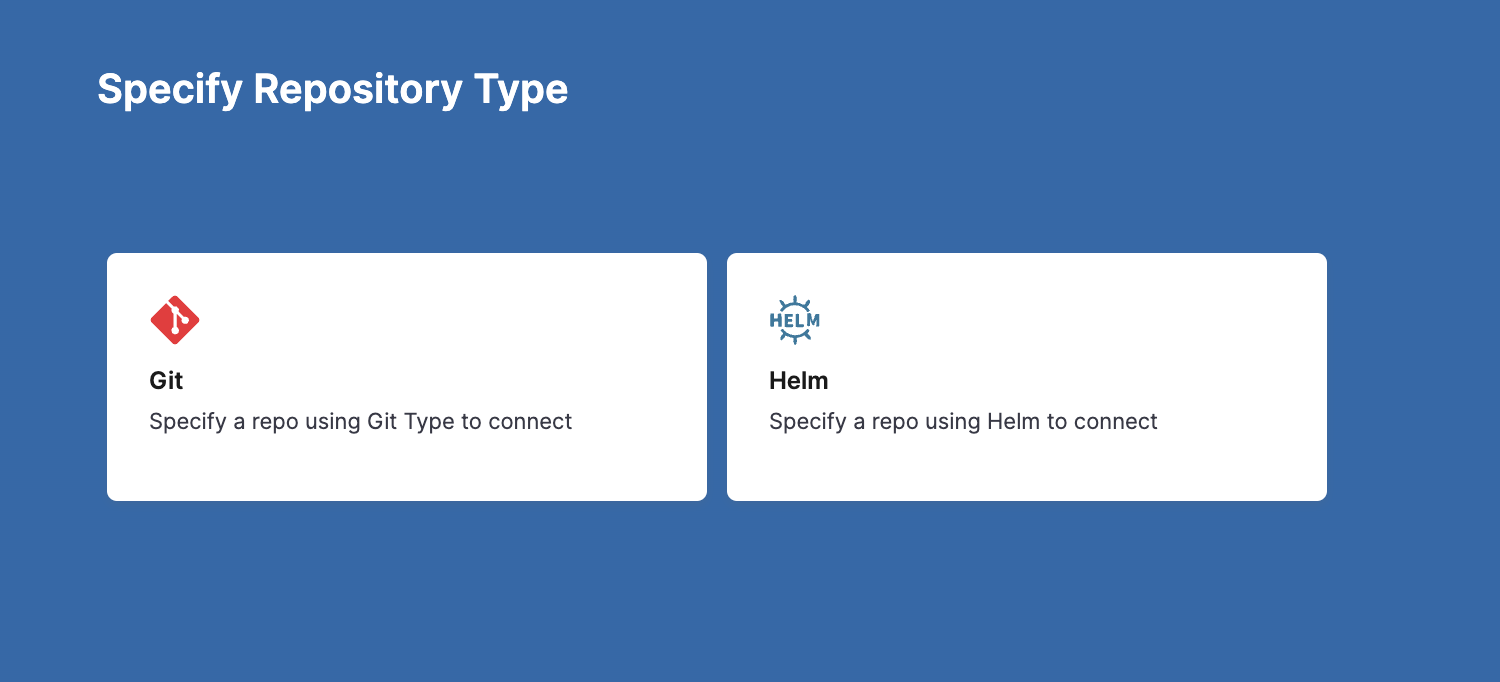
In Specify Repository Type, select:
- Git to add Git repositories.
- Helm to add HTTP Helm and OCI Helm repositories.
- Git providers
- HTTP Helm repository
- OCI Helm repository
- Using a self-signed certificate
- OCI Helm repository with ESO
-
In Specify Repository Type, select Git.
-
In Repository Name, enter a name.
-
In GitOps Agent, select or create the Agent you want to use to fetch manifests from this repo. For details, go to Install a Harness GitOps Agent.
-
In Repository URL, enter the URL to your repo. For example,
https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps.git. -
Select Continue.
-
In Credentials, select one of the following:
-
Specify Credentials for Repository
- In Credentials, in Connection Type, select HTTPS, or SSH, or GitHub App.
- If you use Two-Factor Authentication for your Git repo, you connect over HTTPS or SSH.
- For SSH, ensure that the key is not OpenSSH, but rather PEM format. To generate an SSHv2 key, use:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -m PEMThersaand-m PEMensure the algorithm and that the key is PEM. Next, follow the prompts to create the PEM key. - For more information, see the ssh-keygen man page.
- HTTP also has the Anonymous option. When a repository is configured with an anonymous connection type (public - no credentials), Harness automatically uses the repository credentials if they are available, even if you do not explicitly select them in the UI.
- For steps on setting up the GitHub App, go to Use a GitHub App in a GitHub Connector.
- Select Save & Continue. Harness validates the connection.
- In Credentials, in Connection Type, select HTTPS, or SSH, or GitHub App.
-
Use a Credentials Template
-
Select the GitOps credentials template to use.
For details, go to Harness GitOps Repository Credentials Template.
If you use a repository credentials template for GitOps repository authentication, then the repository path in the GitOps repository must be a subfolder of the repository path in the repository credentials template.
For example, if you created a repository credentials template for the URL
https://something.com, GitOps repositories that have their URL ashttps://something.com/*are able to use that repository credentials template.Harness will auto-detect the repository credentials template (if any) based on the GitOps repository URL and auto-populate it. If Harness auto-populated the GitOps repository, then you cannot edit the repository credentials template setting.
-
-
Skip Server Verification
Select this option to have the GitOps Agent skip verification of the URL and credentials.
Verification is only skipped when you create the GitOps repository. Subsequent uses of the GitOps repository are verified.
-
Enable LFS Support
Select the option to use Git Large File Storage.
-
Proxy
A proxy for your repository can be specified in the proxy setting.
Harness uses this proxy to access the repository. Harness looks for the standard proxy environment variables in the repository server if the custom proxy is absent.
An example repository with proxy:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: private-repo
namespace: cd
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
stringData:
type: git
url: https://github.com/argoproj/private-repo
proxy: https://proxy-server-url:8888
password: my-password
username: my-username -
-
Select Save & Continue. Harness validates the connection.
- In Specify Repository Type, select Helm.
- In Repository Name, enter a name.
- In GitOps Agent, select or create the Agent you want to use to fetch charts from this repo. See Install a Harness GitOps Agent.
- In Repository URL, enter the URL to your HTTP Helm repository. For example,
https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami. - Select Continue.
- In Credentials, select one of the following:
- Specify Credentials for Repository
- In Credentials, in Connection Type, select HTTPS or SSH.
- If you use Two-Factor Authentication for your Git repository, you connect over HTTPS or SSH
- For SSH, ensure that the key is not OpenSSH, but rather PEM format. To generate an SSHv2 key, use:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -m PEM. Thersaand-m PEMensure the algorithm and that the key is PEM. Next, follow the prompts to create the PEM key. - For more information, see the ssh-keygen man page.
- HTTP also has the Anonymous option.
- Select Save & Continue. Harness validates the connection.
- In Credentials, in Connection Type, select HTTPS or SSH.
- Use a Credentials Template
-
Select the GitOps credentials template to use.
For details, go to Harness GitOps Repository Credentials Template.
If you use a repository credentials template for GitOps repository authentication, then the repository path in the GitOps repository must be a subfolder of the repository path in the repository credentials template.
For example, if you created a repository credentials template for the URL
https://something.com, GitOps repositories that have their URL ashttps://something.com/*are able to use that repository credentials template.Harness will auto-detect the repository credentials template (if any) based on the GitOps repository URL and auto-populate it. If Harness auto-populated the GitOps repository, then you cannot edit the repository credentials template setting.
-
- Specify Credentials for Repository
- Select Save & Continue. Harness validates the connection.
- In Specify Repository Type, select Helm.
- In Repository Name, enter a name.
- In GitOps Agent, select or create the Agent you want to use to fetch charts from this repo. For details, go to Install a Harness GitOps Agent.
- In Repository URL, enter the URL to your OCI Helm repository. For example,
registry-1.docker.io/docker. - Select Enable OCI
- Select Continue.
- In Credentials, select Specify Credentials for Repository.
-
In Credentials, in Connection Type, select HTTPS, the Anonymous option to add a public repository.
-
To add a private repository, select the authentication option with username and password, and enter the access token.
This authentication is supported for Docker and GitHub. AWS and Google have short-lived tokens, and might not work as expected. However, if you have an External Secrets Operator installed, you can configure the repository for regenerating tokens. For more information, go to OCI Helm repository with ESO.
-
- Select Save & Continue. Harness validates the connection.
- Credentials Template is not supported for OCI Helm repository.
- Currently, when adding an application with a Helm-based source configured via OCI, the application wizard does not automatically load the available charts. This is a limitation from Argo CD. As a workaround, users must manually specify the chart details when configuring the application.
If you intend to establish an HTTPS connection to a repository and plan to use either a self-signed certificate or one signed by a private Certificate Authority (CA), it is essential to generate the repository certificate prior to setting up the repository itself.
- To create repository certificate:
- In GitOps, in Settings, select Repository Certificates, and then select New Repository Certificate.
- In Repository Type, select TLS Repository Certificate.
- In Repository Server Name, enter the name of the repository server issuing the certificate. For example,
github.mycompany.internal. - Paste the certificate in TLS Certificate (PEM Format). Enclose each certificate in
BEGIN CERTIFICATEandEND CERTIFICATEcomments.
- In Specify Repository Type, select Helm.
- In Repository Name, enter a name.
- In GitOps Agent, select or create the Agent you want to use to fetch charts from this repo. For details, go to Install a Harness GitOps Agent.
- In Repository URL, enter the URL to your OCI Helm repository. For example,
us-east4-docker.pkg.dev/<gcp-project>/<repository>. - Select Enable OCI
- Select Continue.
- In Credentials, select Specify Credentials for Repository.
- Select the authentication option with Username and password,
- In the Username field, if you are authenticating to AWS, enter
AWS. If you are authenticating to Google, enteroauth2accesstoken. - In Password enter your short-lived token (obtained with
aws ecr get-login-passwordfor AWS andgcloud auth print-access-tokenfor Google). If you have an External Secrets Operator, a Refresh token checkbox appears. Enable the checkbox.
- In the Username field, if you are authenticating to AWS, enter
- If you checked Refresh Token, specify a Refresh Interval (for example, 1m, 1h, 12h, or 1d). This is the interval with which you want the token to be refreshed.
- Harness uses the URL you enter to determine whether the registry is a Google or AWS registry. You can select the type of authentication that you want to use with the registry.
- For Google, you can select Google Service Account or Google Workload Identity.
- If you select Google Service Account, you must upload the service account key file. Paste the contents of the file in the Account Key field. Contents of the file must be on a single line. For example:
{ "type": "service_account", "project_id": "google-project-id", "private_key_id": "xxxx70c719xxxxbe7be090083xxxxxd85eca6", "private_key": "...", .... "universe_domain": "googleapis.com" }- If you select Google Workload Identity, you must enter the GCP Workload parameters. For more information, go to Google Workload Identity.
- The
project_idis the project where the registry is located.
- For AWS, you can select AWS Access Credentials or AWS Service Account.
- If you select AWS Access Credentials, enter the AWS access key ID, the AWS secret access key, and, optionally, the AWS session token. For more information, go to AWS Credentials.
- If you select AWS Service Account, enter the service account.
- Region is the region in which the registry is located.
- Role is the role ARN that will be assumed with given credentials.
- For Google, you can select Google Service Account or Google Workload Identity.
- Select the authentication option with Username and password,
- Select Save & Continue. Harness validates the connection.
Credentials Template is not supported for OCI Helm repository.
Skip server verification
Select this option to have the GitOps Agent skip verification of the URL and credentials.
Verification is only skipped when you create the GitOps repository. Subsequent uses of the GitOps repository are verified.
Verify connection
The connection is verified.
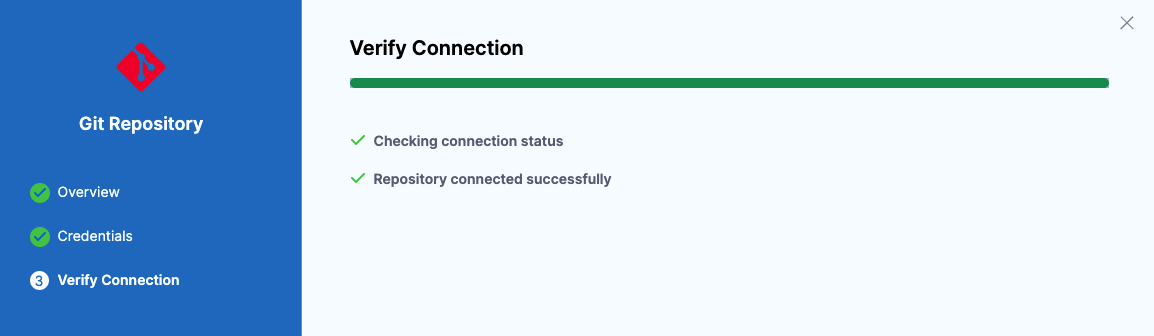
If you encounter errors, check that you have the correct repository URL and your authentication method has the required permissions.
Select Finish. You now have a Harness GitOps repository added.