Cache Intelligence
Modern continuous integration systems execute pipelines inside ephemeral environments that are provisioned solely for pipeline execution and are not reused from prior pipeline runs. As builds often require downloading and installing many library and software dependencies, caching these dependencies for quick retrieval at runtime can save a significant amount of time.
With Cache Intelligence, a Harness CI Intelligence feature, Harness automatically caches and restores software dependencies to speed up your builds - hassle free.
You can use Cache Intelligence with any build infrastructure.
- Cache Intelligence is GA.
- Supported on Cloud and Kubernetes build infrastructure.
- Cache Intelligence is enabled by default for newly created CI stages (configurable in CI Build stage settings.
S3 options via stage variables (applies to both Cache Intelligence and S3 cache steps):
- Path Style: Set
PLUGIN_PATH_STYLE: "true"as a stage variable. This is injected into all steps and used by Cache Intelligence and S3 cache steps. - Encryption: To enable server-side encryption for cache artifacts uploaded to S3, set the encryption stage variables described in Caching with bucket encryption policies. These variables are stage-scoped and affect both Cache Intelligence and S3 cache steps.
Supported tools and paths
Cache Intelligence fully supports Bazel, Maven, Gradle, Yarn, Go, Node, VB (with .Net), F# (with .Net) and MSBuild/dotnet (only for C#) build tools, as long as default cache paths are used.
Below is a list of the default locations cached using Cache Intelligence:
| Build Tool | Dependency Management file | Default Path cached |
|---|---|---|
Maven | pom.xml | .m2/repository |
Gradle | build.gradle | .gradle |
Bazel | WORKSPACE | .bazel |
Node | yarn.lock | .yarn |
Go | go.mod | .go |
C# .Net | *.csproj | .nuget/packages |
VB .Net | *.vbproj | .nuget/packages |
F# .Net | *.fsproj | .nuget/packages |
By default, Cache Intelligence searches for the exact filenames listed in the table above under the Dependency Management file.
Harness Cache Intelligence will explore the root directory as well as one directory depth below for the file to determine the tool that a customer is using in the repository.
This then determines the Default Path Cached location that Harness will save and restore as a part of the Cache Intelligence process.
To make modifications for other build tools or non-default cache locations, use Cache Intelligence with custom cache paths.
Cache storage
When you use Cache Intelligence with Harness CI Cloud, the cache is stored in the Harness-managed environment. When running builds on self-managed infrastructure, you will need to provide your own storage.
- Harness Cloud
- Self-managed build infrastructures
When you use Cache Intelligence with Harness CI Cloud, you don't need to bring your own storage, because the cache is stored in Harness-managed Harness Cloud storage.
All pipelines in the account use the same cache storage, and each build tool has a unique cache key that is used to restore the appropriate cache data at runtime.
The cache storage limit depends on your subscription plan type. Please visit Subscriptions and licenses page to learn more about usage limits.
Harness doesn't limit the number of caches you can store, but, once you reach your storage limit, Harness continues to save new caches by automatically evicting old caches.
The cache retention window is 15 days, which resets whenever a cache is updated.
For blobs larger than 5 GB, multi-part upload (enabled via FF CI_ENABLE_MULTIPART) is used for caching to storage, while standard uploads are used for blobs up to 5 GB.
When running builds in self-managed infrastructures, configure S3-compatible default object storage that Harness can use to seamlessly store and manage the cache.
We suggest that you consider setting bucket level retention policy for efficient cache management.
Enable Cache Intelligence
-
If you're not using Harness Cloud build infrastructure, you must configure S3-compatible global object storage that Harness can use to store and manage caches.
This is not required for Harness Cloud build infrastructure. For more information, go to Cache storage.
-
Enable Cache Intelligence in each applicable stage in your pipeline.
To do this in the Visual editor, select a Build stage, select the stage's Overview tab, and then select Enable Cache Intelligence.
To do this in the YAML editor, add the following to your pipeline's
stage.spec:caching:
enabled: true -
Add custom cache paths if you're using an unsupported build tool, a non-default cache location, or a Windows platform. For a list of supported tools, go to Supported tools and paths.
-
You can also:
Customize cache paths
Cache Intelligence stores the data to be cached in the /harness directory by default. You can use paths to specify a list of locations to be cached. This is useful if:
- You're not using a fully supported build tool.
- You have customized cache locations, such as with
yarn config set cache-folder. - You're using a Windows platform.
When using custom paths, you must also provide a cache key. If a cache path is specified without a key, Cache Intelligence will be disabled, skipping cache operations.
- Visual editor
- YAML editor
-
In the same stage where you enabled Cache Intelligence, go to the Overview tab, and make sure Enable Cache Intelligence is selected.
-
In Paths, specify cache paths.
On Windows platforms, you might need to specify the cache path from
C:, such asC:\harness\node_modules.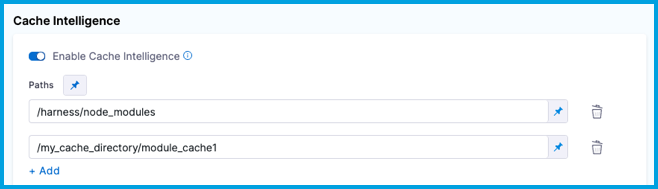
-
Cache paths outside the
/harnessdirectory must also be declared in Shared Paths.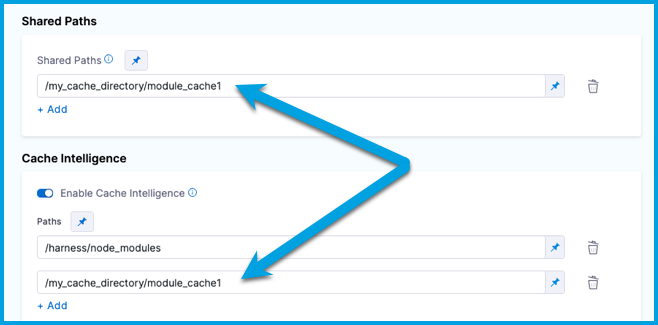
In the same stage where you enabled Cache Intelligence, add a list of paths to cache under stage.spec.caching. For example:
- stage:
name: Build
identifier: Build
type: CI
spec:
caching:
enabled: true
paths:
- /harness/node_modules
cloneCodebase: true
On Windows platforms, you might need to specify the cache path from C:, such as C:\harness\node_modules.
Cache paths outside the /harness directory must also be declared in shared paths. Add the list of sharedPaths under stage.spec, for example:
- stage:
name: Build
identifier: Build
type: CI
spec:
caching:
enabled: true
paths: # All custom cache paths.
- /harness/node_modules # Custom cache path within /harness directory.
- /my_cache_directory/module_cache1 # Custom cache path outside /harness directory.
cloneCodebase: true
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Amd64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
sharedPaths: # All shared paths outside /harness directory. These can be cache paths or other shared paths for your pipeline.
- /my_cache_directory/module_cache1 # Custom cache path outside /harness directory.
Customize cache keys
Harness generates a cache key from a hash of the build lock file (such as pom.xml, build.gradle, or package.json) that Harness detects. If Harness detects multiple tools or multiple lock files, Harness combines the hashes to create the cache key.
You can define custom cache keys if you don't want to use the default cache key naming behavior or you have a use case that requires defining custom cache keys, such as caching in parallel stages.
When Cache Intelligence is enabled, the cache plugin automatically detects build tools and determines cache paths, unless custom paths are specified. Cache paths are stored under <account_id>/default/path/to/directory.
- Visual
- YAML
-
In the same stage where you enabled Cache Intelligence, go to the Overview tab, and make sure Enable Cache Intelligence is selected.
-
Enter the custom key value in Key.
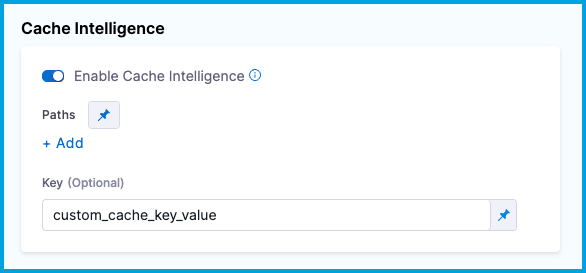
To customize the cache key in the YAML editor, add key: CUSTOM_KEY_VALUE under stage.spec.caching in the same stage where you enabled Cache Intelligence.
- stage:
name: Build
identifier: Build
type: CI
spec:
caching:
enabled: true
key: <+input> # This example uses runtime input so that the user specifies the cache key at runtime.
cloneCodebase: true
You can use fixed values, runtime inputs, and expressions for the key value.
Cache Intelligence in parallel stages
If you have multiple stages that run in parallel, you must use custom cache keys for each stage that uses Cache Intelligence. This prevents conflicts when the parallel stages attempt to save or retrieve caches concurrently.
If your stage uses a matrix or repeat looping strategy that generates multiple stage instances, you can construct a key using a Harness expression to generate unique cache keys, such as prefix-{{ checksum "<filename>" }}-<+matrix.axesName>. The <+matrix.axesName> expression references the axes name ensuring a unique key for the cell. Follow the snippet below for an example:
- stage:
name: Build
identifier: Build
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
caching:
enabled: true
override: true
key: cache-{{ checksum "build.gradle" }}-<+matrix.javaVersion>
This produces a unique cache key for the matrix like so:
key=cache-f6811cecc83b9b3889c41e720d5ee4a5-17/.gradle
key=cache-f6811cecc83b9b3889c41e720d5ee4a5-21/.gradle
Define cache policy
The cache policy defines how you use caching in a stage.
For example, if your pipeline has two stages, you might want to restore the cache in the first stage and then save the cache in the second stage, rather than both saving and restoring the cache in both stages.
To configure the cache policy, add policy: pull | push | pull-push to stage.spec.caching.
policy: pull- Only restore cache.policy: push- Only save cache.policy: pull-push- Save and restore cache. This is the default setting.
For example, here is a pipeline with two Build (CI) stages using Cache Intelligence. The first stage's cache policy is set to pull only, and the second stage's cache policy is set to push only. When this pipeline runs, the first stage restores the build cache, and the second stage saves the cache at the end of the build.
stages:
- stage:
name: buildStage1
identifier: buildstage1
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Amd64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
caching:
enabled: true
policy: pull # Define cache policy.
execution:
steps:
...
- stage:
name: buildStage2
identifier: buildstage2
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Amd64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
caching:
enabled: true
policy: push # Define cache policy.
execution:
steps:
...
Enable cache override
The cache override allows you to force push the cache even if the cache key hasn't changed.
By default, cache override is set to true regardless of cache changes. This is useful if you have infrequent builds and want to ensure your cache remains fresh. You can change the default behaviour in CI default settings.
To configure the cache override, add override: true | false to stage.spec.caching.
override: true- Always save the cache. Currently, this is the default setting.override: false- Only save the cache if there are changes.
For example:
- stage:
name: Build
identifier: Build
type: CI
spec:
caching:
enabled: true
override: false # Define cache override.
cloneCodebase: true
Cache Intelligence API
You can use the Cache Intelligence API to get information about the cache or delete the cache.
API key authentication is required. You need a Harness API key with core_account_edit permission. For more information about API keys, go to Manage API keys. For more information about authentication, go to the Harness API documentation.
Get cache metadata
Get metadata about the cache, such as the size and path.
curl --location --request GET 'https://app.harness.io/gateway/ci/cache/info?accountIdentifier=$YOUR_HARNESS_ACCOUNT_ID' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'X-API-KEY: $API_KEY'
Delete cache
Delete the entire cache, or use the optional path parameter to delete a specific subdirectory in the cache.
curl --location --request DELETE 'https://app.harness.io/gateway/ci/cache?accountIdentifier=$YOUR_HARNESS_ACCOUNT_ID&path=/path/to/deleted/directory' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'X-API-KEY: $API_KEY'
Troubleshoot caching
Ignoring Cache Intel Directories in Apache RAT Scans
If you are using the Apache RAT plugin for license compliance, it may incorrectly mark Harness Cache Intelligence directories as invalid files. This can cause unnecessary failures in your build pipeline.
To avoid this, explicitly exclude the following directories in your pom.xml file.
Directories to Ignore
-
Build Intelligence:
/harness/.mvn -
Cache Intelligence:
/harness/.m2/harness/.mvn(also applies to cache-related scans)
Example: Update to pom.xml
Add the following snippet under the <build> section to configure the apache-rat-plugin to ignore these paths:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.rat</groupId>
<artifactId>apache-rat-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.15</version> <!-- Or use the latest version -->
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>/harness/.mvn</exclude>
<exclude>/harness/.m2</exclude> <!-- Optional, but recommended -->
</excludes>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>verify</phase>
<goals>
<goal>check</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
Gradle cache location
Harness sets the following environment variable for Gradle builds:
GRADLE_USER_HOME=/harness/.gradle
As a result:
- All Gradle dependencies and caches are saved and restored from
/harness/.gradlebecause/harnessis a shared directory that can be accessed across all steps. - Cache Intelligence and the Save/Restore Cache steps are optimized for this path.
- This location is different from the default Gradle cache location (
~/.gradle).
Cache Intelligence is not currently supported on local (self-managed) infrastructure.
Go to the CI Knowledge Base for questions and issues related to caching, data sharing, dependency management, workspaces, shared paths, and more. For example: