Configure codebase
CI pipelines build and test code that is pulled from a Git code repository. In Harness CI, you can configure a 'Codebase' for your pipeline, to define the Git repository your Build stage(s) will automatically clone during runtime (unless you stage is set to not clone the codebase). When you add a Build stage to a CI pipeline, if not already set, you will have to option to configure your codebase. This topic explains how to configure codebase settings for pipeline to be used by its Build stages.
This topic assumes you have an understanding of the CI pipeline creation process.
Configure the default codebase
When you add a Build stage to a CI pipeline, you specify where your build code is stored. This becomes the pipeline's default codebase.
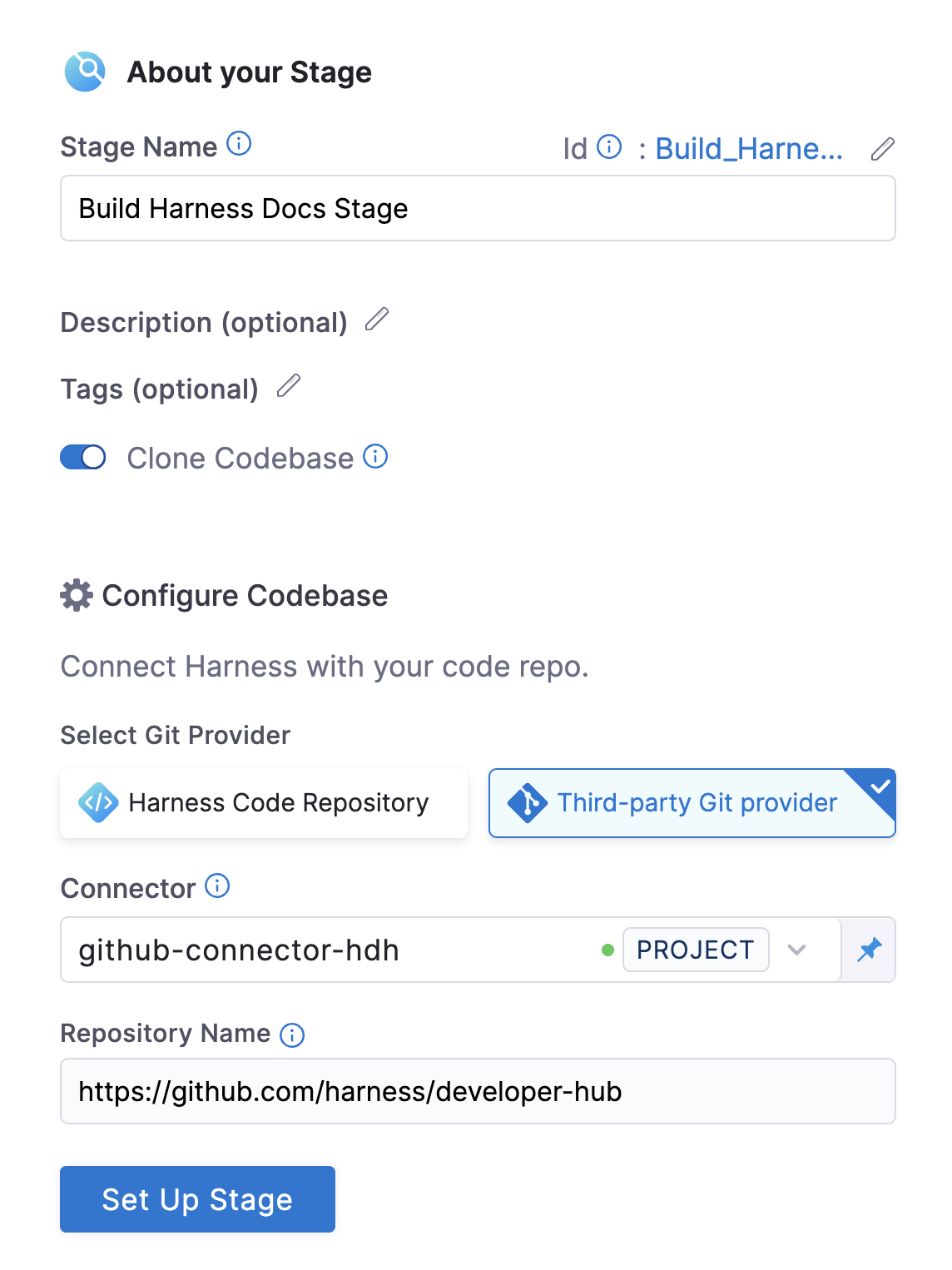
- In the Pipeline Studio, select Add Stage, and then select Build.
- Enter a Stage Name. Description and Tags are optional.
- Make sure Clone Codebase is enabled. This tells Harness to clone the codebase into the build environment before running the steps in the stage.
tip
In VM runners and cloud infrastructure, the step to clone your codebase runs in a container by default. Enable the
CI_GIT_CLONE_CONTAINERLESSfeature flag to run it on the host, which is recommended for faster cloning on Windows by eliminating image download time. - Configure your codebase connection.
- To clone a repo from the Harness Code Repository module, select Harness Code Repository, and then select the repo to clone.
- To clone a repo from a third-party Git provider, select Third-party Git provider, select the relevant code repo connector, and enter the name of the repo to clone, if Repository Name is not automatically populated.
- Select Set Up Stage.
If you need to change the connector or other default codebase settings, go to Edit the default codebase configuration. If you don't want every stage to clone the default codebase, go to Disable Clone Codebase for specific stages. You can also clone multiple repositories in a stage.
YAML example: Default codebase configuration
pipeline:
name: tutorial example
identifier: tutorial_example
projectIdentifier: default
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
properties:
ci:
codebase:
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
build: <+input>
YAML example: Harness Code Repository codebase configuration
This configuration is for repositories in the Harness Code Repository module.
pipeline:
name: tutorial example
identifier: tutorial_example
projectIdentifier: default
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
properties:
ci:
codebase:
repoName: YOUR_HARNESS_CODE_REPO_NAME
build: <+input>
Disable Clone Codebase for specific stages
After defining the default codebase in the first Build stage, when you add subsequent stages to the pipeline, you can disable Clone Codebase for individual stages. You can also disable cloning the default codebase, if necessary.
You might disable Clone Codebase if the codebase is not needed for the stage's operations, or you need to use specific git clone arguments (such as to clone a subdirectory instead of an entire repo). You can also clone multiple code repos in a pipeline.
In the Visual editor, you can disable Clone Codebase in the stage's Overview tab.
In the YAML editor, set cloneCodebase to false in the stage.spec.
- stage:
name: build
identifier: build
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: false
For more information about Build stage settings, go to CI Build stage settings.
Edit the default codebase configuration
Git Clone enhancements listed below are now Generally Available (GA)
Harness has introduced several powerful enhancements to Git clone operations, available in both the Git Clone step and the native Clone Codebase functionality. These include:
- Git LFS - Allows users to clone repositories with large file storage (LFS) efficiently.
- Fetch Tags - Enables fetching of tags during the clone operation.
- Sparse Checkout - Enables cloning specific subdirectories.
- Clone Submodules - Adds options for including and recursively cloning Git submodules.
- Clone Path Customization - Exposes the clone path in the codebase section, allowing users to specify a custom clone directory.
- Additional Pre-Fetch Command - Ability to specify any additional Git commands to run before fetching the code.
If these capabilities are not yet enabled in your account, please reach out to Harness Support for assistance.
- Visual
- YAML
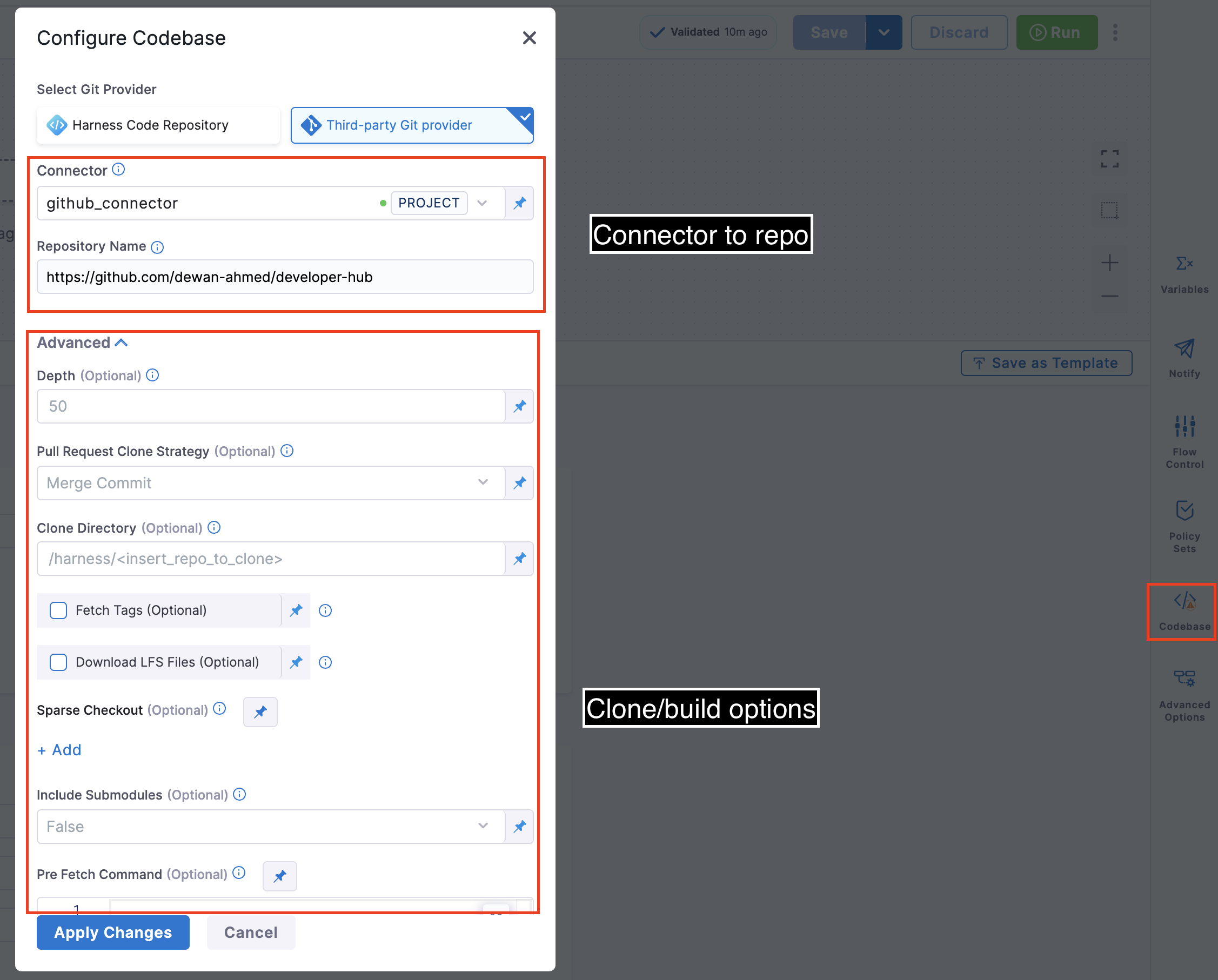
To edit a pipeline's default codebase configuration, select Codebase on the right side panel of the Pipeline Studio's Visual editor.
To edit a pipeline's default codebase configuration in the YAML editor, edit the codebase section. For example:
pipeline:
name: tutorial example
identifier: tutorial_example
projectIdentifier: tutorial_test
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
properties:
ci:
codebase:
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
build: <+input>
depth: 0
sslVerify: true
prCloneStrategy: MergeCommit
In addition to changing the Connector (connectorRef) or Repository Name (repoName), you can edit the following Advanced settings.
Depth
The number of commits to fetch when the pipeline clones the codebase repo.
The default depth varies by build and trigger type:
- For manually-triggered branch and tag builds, the default depth is
50. This means eachgit cloneoperation fetches the 50 most recent commits. - For manually-triggered PR builds and all auto-triggered builds (such as webhook triggers), the default depth is
0. This means eachgit cloneoperation fetches all commits from the relevant branch.
For more information, go to the git clone documentation.
Pull Request Clone Strategy
When a build is triggered by a pull request, this setting determines the branch to use for the artifact after the repo is cloned.
If this is set to Merge Commit (which is the default setting), the pipeline tries to merge the pull request branch with the target branch before building the artifact. This guarantees that the artifact includes all commits in both the pull request and the target branch. The disadvantage is that this can take more time and result in build failures: If the merge fails, then the build fails.
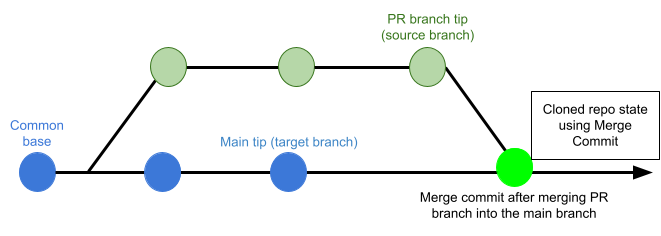
If this is set to Source Branch, the pipeline builds the artifact from the latest commit in the pull request branch. This can be faster and less likely to result in build failures; however, it might not include some commits in the target branch.
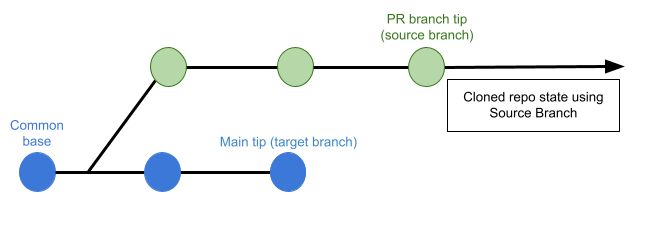
Clone Directory
An optional target path in the pipeline workspace where you want to clone the repo.
You can't specify /harness/ as a target directory for a Git Clone step because this folder is reserved for the Build stage's codebase. You can specify Shared Paths in your CI Build stage settings to share data across steps in your Build stage.
On Harness macOS build infrastructure, /harness is a protected system directory. The workspace is /tmp/harness instead (/tmp/harness is a symlink to /private/tmp/harness; both paths work). If you use macOS infrastructure, specify clone directory paths using either the full macOS workspace path (for example, /tmp/harness/my-repo) or a relative path (for example, ./my-repo). For more information, go to How can I share cache between different OS types?.
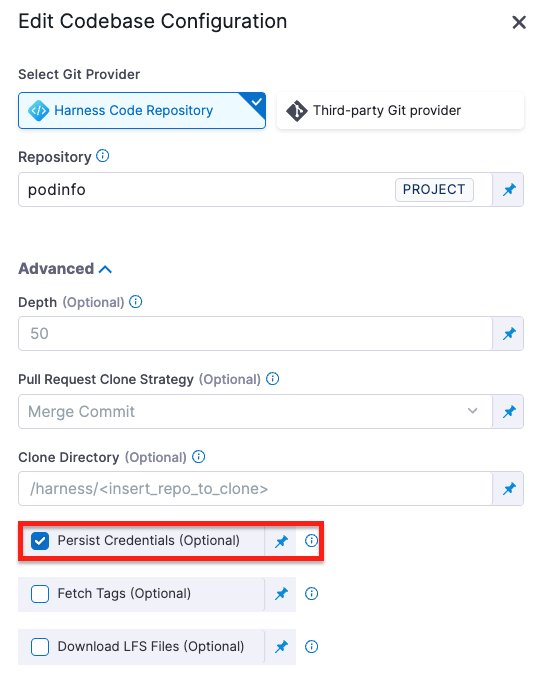
Persist Credentials (Optional)
When selected, Harness persists the Git credentials used during the clone step so they remain available for subsequent steps in the same build.
This is useful when:
-
You need to run Git commands (for example, fetching submodules, tagging, or pushing commits) after the clone step.
-
You’re using a private Harness Code Repository or authenticated third-party repository, and you want to avoid re-authenticating in every step.
The persisted credentials remain available only within the scope of the build environment (container or VM) for the duration of the build. They are not stored or reused after the build completes.
Fetch Tags
Determines whether to fetch all tags when performing a shallow clone (depth > 0). Setting this to true is equivalent to adding the --tags flag.
Download LFS Files
The Git Large File Storage (LFS) client is an extension for versioning large files, such as audio, video, datasets, and graphics.
Set Download LFS Files to true to download Git-LFS files. Default is false.
Sparse Checkout
Do a sparse checkout on given patterns. The subset of files is chosen by providing a list of directories in cone mode. Refer to git documentation for more details.
Include Submodules
Determines whether to include submodules in the clone. Default is false. Set to true to include submodules or recursive to clone submodules recursively.
Pre Fetch Command
Specify any additional Git commands to run before fetching the code. This field is for Git commands only; separate each command with a new line.
This could be used, for example, to set additional LFS configurations or clone specific submodules. For example,
git config lfs.fetchexclude ".jpg"
SSL Verify
If True, which is the default value, the pipeline verifies your Git SSL certificates. The build fails if the certificate check fails. Set this to False only if you have a known issue with the certificate and you are willing to run your builds anyway.
If you want to use self-signed certificates in a Kubernetes Cluster build infrastructure, go to Configure a Kubernetes Build Farm to use Self-Signed Certificates
Set Container Resources
Set maximum resource limits for the containers that clone the codebase at runtime:
- Limit Memory: The maximum memory that the container can use. You can express memory as a plain integer or as a fixed-point number using the suffixes
GorM. You can also use the power-of-two equivalentsGiandMi. The default is500Mi. - Limit CPU: The maximum number of cores that the container can use. CPU limits are measured in CPU units. Fractional requests are allowed; for example, you can specify one hundred millicpu as
0.1or100m. The default is400m. For more information, go to Resource units in Kubernetes.
Troubleshoot codebases
Go to the Harness CI Knowledge Base for common questions and issues related to codebases, such as:
- How do I improve codebase clone time?
- The same Git commit is not used in all stages.
- Git fetch fails with invalid index-pack output when cloning large repos.
- Clone codebase fails due to missing plugin.
For information about branch protection and status checks for codebases associated with Harness CI pipelines, go to SCM status checks.
For troubleshooting information for Git event (webhook) triggers, go to Troubleshoot Git event triggers.