Environment Blueprints in Harness IDP
An Environment Blueprint is a collection of infrastructure templates, services, their configurations and lifecycle management details of each. When a blueprint is orchestrated, it generates running instances of Environments. Blueprints are typically owned by the Platform Engineering team.
Environment Blueprint YAML
An Environment Blueprint is defined using a declarative YAML format. The YAML structure defines infrastructure templates, services, dependencies, and lifecycle management for environments.
Core Components
An environment blueprint YAML has the following core components:
1. API Definition
apiVersion: Alwaysharness.io/v1for Environment Blueprintskind: Must beEnvironmentBlueprintname: Human-readable name for the blueprintidentifier: Unique identifier for the blueprint (auto-generated)owner: Access control specification (group or user)
2. Specification (spec)
entities: List of infrastructure, service components and other entitiesinputs: User-configurable parameters for the blueprint
apiVersion: harness.io/v1
kind: EnvironmentBlueprint
type: ''
name: <blueprint-name>
identifier: <blueprint-identifier>
owner: group:account/_account_all_users
spec:
entities: []
inputs: {}
Entity Specification
Each entity in an Environment Blueprint represents a component (infrastructure or service) that will be provisioned or deployed. Entities are the building blocks that define what gets created and how they interact with each other.
Entity Structure
Each entity in the blueprint is composed of 2 main parts:
1. Backend - Describes the lifecycle implementation of the entity
- Defines how the entity is provisioned, deployed, or managed
- Specifies the backend type (
HarnessIACMfor infrastructure,Catalogfor services). Go to Backend Types to learn more. - Contains configuration values and operational steps
2. Interface - Defines how the entity relates to other entities specified in the blueprint
- Declares dependencies on other entities
- Specifies entity-level user-configurable inputs
- Defines the entity's interaction model
entities:
- identifier: <entity-name>
interface: # How entity relates to others
dependencies: [] # List of entities this depends on
inputs: {} # User-configurable parameters
backend: # Lifecycle implementation
type: <backend-type> # HarnessIACM or Catalog
values: {} # Configuration and settings
steps: {} # Operational steps (for IaCM)
Entity Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
identifier | string | Unique name for the entity within the blueprint | namespace, frontend, backend |
interface | object | Defines entity relationships and user inputs | See Interface Parameters below |
backend | object | Defines the lifecycle implementation of the entity | See Backend Parameters below |
Interface Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
dependencies | array | List of entity identifiers this entity depends on | [{"identifier": "namespace"}] |
inputs | object | User-configurable parameters with types and defaults at the entity level | {"replicas": {"type": "integer", "default": 1}} |
Backend Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
type | string | Backend type for entity provisioning | HarnessIACM, Catalog |
values | object | Configuration settings specific to the backend type | Varies by backend type |
steps | object | Operational steps for lifecycle management (IaCM only) | {"create": {"template": "MyTemplate"}} |
Backend Types
Environment Blueprints support two main backend types:
1. HarnessIACM Backend (Infrastructure)
Used for provisioning infrastructure resources using Infrastructure as Code Management.
In this definition, backend.type is set to HarnessIACM.
YAML Structure
entities:
- identifier: namespace
backend:
type: HarnessIACM
values:
workspace: Namespace-${{env.config.name}}
steps:
create:
template: TempNamespace # Workspace Template ID
version: '1'
apply:
pipeline: DefaultProvision # Provision pipeline ID
variables:
name: temp-${{env.config.name}}
destroy:
pipeline: DefaultDestroy # Destroy pipeline ID
variables:
name: temp-${{env.config.name}}
delete: {}
pause: {}
resume: {}
HarnessIACM Backend Parameters (backend.values)
| Parameter | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
workspace | string | Workspace name for IaCM operations | Namespace-${{env.config.name}} |
HarnessIACM Backend Steps (backend.steps)
| Step | Required | Description | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
apply | Yes | Provisions infrastructure with "upsert" behavior - creates initially and updates on changes | pipeline, variables |
destroy | Yes | Destroys previously provisioned infrastructure | pipeline, variables |
create | No | Initializes infrastructure (e.g., IaCM Workspace) before first provisioning | template, version |
delete | No | Deletes initialized but unprovisioned infrastructure | None |
Step Dependencies:
createmust be executed before firstapplyoperationdeletemust be executed afterdestroyoperationcreateanddeletesteps must be used together (both or neither)
Example Configuration:
steps:
create:
template: TempNamespace
version: '1'
apply:
pipeline: DefaultProvision
variables:
name: temp-${{env.config.name}}
destroy:
pipeline: DefaultDestroy
variables:
name: temp-${{env.config.name}}
delete: {}
2. Catalog Backend (Services)
Used for deploying application services from the IDP catalog.
In this definition, backend.type is set to Catalog.
YAML Structure
entities:
- identifier: frontend
interface:
dependencies:
- identifier: namespace # Depends on infrastructure
inputs:
version:
type: string
default: v1.1.0
replicas:
type: integer
default: 1
backend:
type: Catalog
values:
identifier: frontend # Component ID from catalog
variables:
replicas: ${{entity.config.replicas}}
version: ${{entity.config.version}}
environment:
identifier: mycluster
infra:
identifier: ssemteamdelegate
namespace: ${{dependencies.namespace.output.name}}
steps:
apply:
pipeline: DeployService
destroy:
pipeline: UninstallService
Catalog Backend (backend.values)
| Parameter | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
identifier | string | Component (service) ID from the IDP catalog | frontend, backend |
variables | object | Input variables passed to the component | {"replicas": "${{entity.config.replicas}}"} |
environment | object | Target deployment environment specification | See environment parameters below |
Environment Parameters (backend.values.environment)
| Parameter | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
identifier | string | CD Service Environment identifier where services will be deployed | mycluster |
infra | object | Infrastructure specification within the environment | See infra parameters below |
Infrastructure Parameters (backend.values.environment.infra)
| Parameter | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
identifier | string | Infrastructure identifier | ssemteamdelegate |
Catalog Backend Steps (backend.steps)
| Step | Required | Description | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
apply | Yes | Deploys the service using the specified pipeline | pipeline |
destroy | Yes | Removes the deployed service using the specified pipeline | pipeline |
Configure TTL (time-to-live)
You can configure TTL for environments in the environment blueprint. Defining a TTL specifies how long an environment can run before it is automatically paused. This helps control costs and prevents lingering environments.
Based on the TTL specification, there are two environment types: Ephemeral and Long-lived. Go to Types of Environments to learn more.
Set TTL in an Environment Blueprint
To define a TTL, add the spec.ttl field to the environment blueprint YAML. The ttl field is specified as follows:
1. TTL specification
spec:
ttl:
kind: <ttl-kind>
default: <default-ttl-duration> # Optional
max: <max-ttl-duration> # Optional
Durations support hours, minutes, and seconds (e.g., 1h, 30m, 1h30m).
2. TTL kinds
fixed— A fixed, preconfigured duration in the blueprint. Users cannot change it when creating an environment.custom— A user-configurable duration chosen at environment creation time.none— No TTL. The environment is long-lived and is only paused/stopped when a user does so explicitly.
3. TTL parameters
default— The default TTL duration for the blueprint (optional).max— The maximum allowed TTL duration for the blueprint (optional).
4. Examples
Fixed 1-hour TTL; the environment pauses automatically after 1 hour:
spec:
ttl:
kind: fixed
default: 1h
max: 24h
User-defined TTL with a default of 3 hours (if no input is provided) and a 24-hour cap:
spec:
ttl:
kind: custom
default: 3h
max: 24h
Long-lived environment (no automatic pause):
spec:
ttl:
kind: none
Note: When you update an environment’s configuration, the environment is re-provisioned and the TTL is reset. The new TTL countdown starts from the time of the update.
YAML Templating System
Environment Blueprints use a powerful templating system for dynamic configuration:
Template Variables
| Variable Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Environment Config | ${{env.config.name}} | Access environment-level inputs |
| Entity Config | ${{entity.config.replicas}} | Access entity-specific inputs |
| Dependency Outputs | ${{dependencies.namespace.output.name}} | Reference outputs from dependent entities |
Example Usage
# Dynamic workspace naming
workspace: Namespace-${{env.config.name}}
# Variable mapping from inputs
variables:
replicas: ${{entity.config.replicas}}
version: ${{entity.config.version}}
# Dependency resolution
namespace: ${{dependencies.namespace.output.name}}
Scope & Hierarchy
Environment Blueprints live at the account scope, while environments can only be created at the project scope.
In an environment blueprint, all the entities, workspace templates, pipelines, etc. are also created at the project scope.
Environment Management RBAC
Harness IDP provides granular Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for environment management, allowing you to control who can view, create, edit, or delete environment blueprints and environments. The RBAC model follows the Harness platform hierarchy with different scopes for blueprints and environments.
Permissions Hierarchy
The environment management RBAC is structured across two main resource types:
| Resource Type | Scope | Available Permissions | Resource Group Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environment Blueprint | Account Level |
|
|
| Environment | Project Level |
|
|
For a complete overview of all IDP resources and their permissions across different scopes, refer to the Permissions & Resources table in the IDP RBAC documentation.
Configuring RBAC for Environment Management
To configure access control for environment management:
-
For Environment Blueprints (Account Level):
- Navigate to Account Settings > Access Control > Roles
- Create or edit a role and assign Environment Blueprint permissions (VIEW, CREATE/EDIT, DELETE)
- Create a Resource Group and select either:
- All Environment Blueprints - Grants access to all blueprints in the account
- Specific Environment Blueprints - Grants access to selected blueprints only
- Assign the role and resource group to users or user groups
-
For Environments (Project Level):
- Navigate to Project Settings > Access Control > Roles
- Create or edit a role and assign Environment permissions (VIEW, CREATE/EDIT, DELETE)
- Create a Resource Group and select either:
- All Environments - Grants access to all environments in the project
- Specific Environments - Grants access to selected environments only
- Assign the role and resource group to users or user groups
For more information on configuring RBAC in Harness, refer to the RBAC documentation.
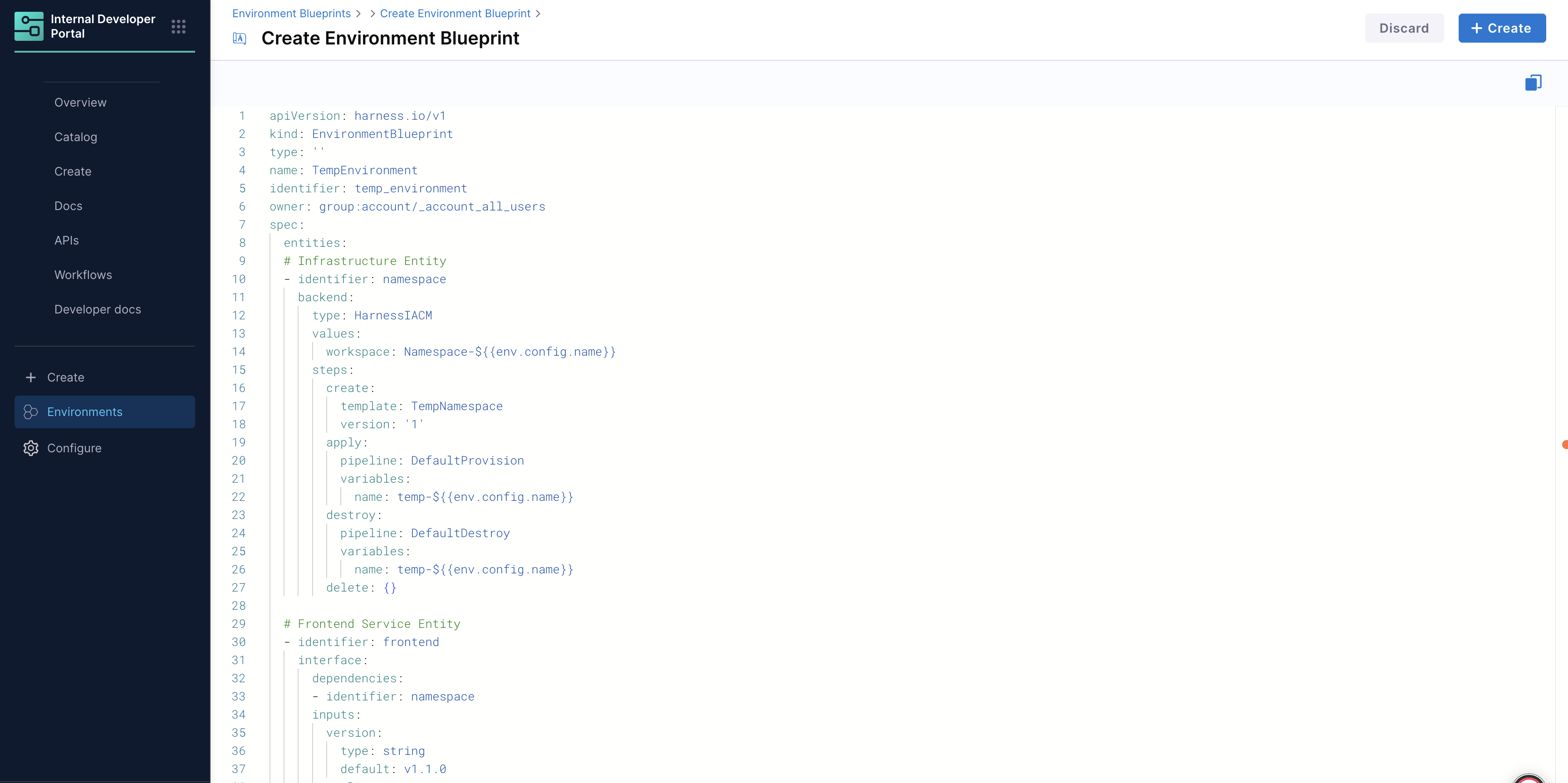
Example Blueprint YAML
apiVersion: harness.io/v1
kind: EnvironmentBlueprint
type: ''
name: TempEnvironment
identifier: temp_environment
owner: group:account/_account_all_users
spec:
entities:
# Infrastructure Entity
- identifier: namespace
backend:
type: HarnessIACM
values:
workspace: Namespace-${{env.config.name}}
steps:
create:
template: TempNamespace
version: '1'
apply:
pipeline: DefaultProvision
variables:
name: temp-${{env.config.name}}
destroy:
pipeline: DefaultDestroy
variables:
name: temp-${{env.config.name}}
delete: {}
# Frontend Service Entity
- identifier: frontend
interface:
dependencies:
- identifier: namespace
inputs:
version:
type: string
default: v1.1.0
replicas:
type: integer
default: 1
backend:
type: Catalog
values:
identifier: frontend
variables:
replicas: ${{entity.config.replicas}}
version: ${{entity.config.version}}
environment:
identifier: mycluster
infra:
identifier: ssemteamdelegate
namespace: ${{dependencies.namespace.output.name}}
steps:
apply:
pipeline: DeployService
destroy:
pipeline: UninstallService
# Backend Service Entity
- identifier: backend
interface:
dependencies:
- identifier: namespace
inputs:
version:
type: string
default: v1.3.2
replicas:
type: integer
default: 1
backend:
type: Catalog
values:
identifier: backend
variables:
replicas: ${{entity.config.replicas}}
version: ${{entity.config.version}}
environment:
identifier: mycluster
infra:
identifier: ssemteamdelegate
namespace: ${{dependencies.namespace.output.name}}
steps:
apply:
pipeline: DeployService
destroy:
pipeline: UninstallService
# Blueprint-level inputs
inputs:
name:
type: string
default: demo
Create Environment Blueprints
In Harness IDP (Environments), navigate to the Environments section, and hit “Create” and then “Environment Blueprint”. Use the YAML provided above to create the environment blueprint.